- Dutch
- Frisian
- Saterfrisian
- Afrikaans
-
- Phonology
- Segment inventory
- Phonotactics
- Phonological processes
- Phonology-morphology interface
- Word stress
- Primary stress in simplex words
- Monomorphemic words
- Diachronic aspects
- Generalizations on stress placement
- Default penultimate stress
- Lexical stress
- The closed penult restriction
- Final closed syllables
- The diphthong restriction
- Superheavy syllables (SHS)
- The three-syllable window
- Segmental restrictions
- Phonetic correlates
- Stress shifts in loanwords
- Quantity-sensitivity
- Secondary stress
- Vowel reduction in unstressed syllables
- Stress in complex words
- Primary stress in simplex words
- Accent & intonation
- Clitics
- Spelling
- Morphology
- Word formation
- Compounding
- Nominal compounds
- Verbal compounds
- Adjectival compounds
- Affixoids
- Coordinative compounds
- Synthetic compounds
- Reduplicative compounds
- Phrase-based compounds
- Elative compounds
- Exocentric compounds
- Linking elements
- Separable complex verbs (SCVs)
- Gapping of complex words
- Particle verbs
- Copulative compounds
- Derivation
- Numerals
- Derivation: inputs and input restrictions
- The meaning of affixes
- Non-native morphology
- Cohering and non-cohering affixes
- Prefixation
- Suffixation
- Nominal suffixation: person nouns
- Conversion
- Pseudo-participles
- Bound forms
- Nouns
- Nominal prefixes
- Nominal suffixes
- -aal and -eel
- -aar
- -aard
- -aat
- -air
- -aris
- -ast
- Diminutives
- -dom
- -een
- -ees
- -el (nominal)
- -elaar
- -enis
- -er (nominal)
- -erd
- -erik
- -es
- -eur
- -euse
- ge...te
- -heid
- -iaan, -aan
- -ief
- -iek
- -ier
- -ier (French)
- -ière
- -iet
- -igheid
- -ij and allomorphs
- -ijn
- -in
- -ing
- -isme
- -ist
- -iteit
- -ling
- -oir
- -oot
- -rice
- -schap
- -schap (de)
- -schap (het)
- -sel
- -st
- -ster
- -t
- -tal
- -te
- -voud
- Verbs
- Adjectives
- Adverbs
- Univerbation
- Neo-classical word formation
- Construction-dependent morphology
- Morphological productivity
- Compounding
- Inflection
- Inflection and derivation
- Allomorphy
- The interface between phonology and morphology
- Word formation
- Syntax
- Preface and acknowledgements
- Verbs and Verb Phrases
- 1 Characterization and classification
- 2 Projection of verb phrases I:Argument structure
- 3 Projection of verb phrases II:Verb frame alternations
- Introduction
- 3.1. Main types
- 3.2. Alternations involving the external argument
- 3.3. Alternations of noun phrases and PPs
- 3.3.1. Dative/PP alternations (dative shift)
- 3.3.1.1. Dative alternation with aan-phrases (recipients)
- 3.3.1.2. Dative alternation with naar-phrases (goals)
- 3.3.1.3. Dative alternation with van-phrases (sources)
- 3.3.1.4. Dative alternation with bij-phrases (possessors)
- 3.3.1.5. Dative alternation with voor-phrases (benefactives)
- 3.3.1.6. Conclusion
- 3.3.1.7. Bibliographical notes
- 3.3.2. Accusative/PP alternations
- 3.3.3. Nominative/PP alternations
- 3.3.1. Dative/PP alternations (dative shift)
- 3.4. Some apparent cases of verb frame alternation
- 3.5. Bibliographical notes
- 4 Projection of verb phrases IIIa:Selection of clauses/verb phrases
- 5 Projection of verb phrases IIIb:Argument and complementive clauses
- Introduction
- 5.1. Finite argument clauses
- 5.2. Infinitival argument clauses
- 5.3. Complementive clauses
- 6 Projection of verb phrases IIIc:Complements of non-main verbs
- 7 Projection of verb phrases IIId:Verb clusters
- 8 Projection of verb phrases IV: Adverbial modification
- 9 Word order in the clause I:General introduction
- 10 Word order in the clause II:Position of the finite verb (verb-first/second)
- 11 Word order in the clause III:Clause-initial position (wh-movement)
- Introduction
- 11.1. The formation of V1- and V2-clauses
- 11.2. Clause-initial position remains (phonetically) empty
- 11.3. Clause-initial position is filled
- 12 Word order in the clause IV:Postverbal field (extraposition)
- 13 Word order in the clause V: Middle field (scrambling)
- 14 Main-clause external elements
- Nouns and Noun Phrases
- 1 Characterization and classification
- 2 Projection of noun phrases I: complementation
- Introduction
- 2.1. General observations
- 2.2. Prepositional and nominal complements
- 2.3. Clausal complements
- 2.4. Bibliographical notes
- 3 Projection of noun phrases II: modification
- Introduction
- 3.1. Restrictive and non-restrictive modifiers
- 3.2. Premodification
- 3.3. Postmodification
- 3.3.1. Adpositional phrases
- 3.3.2. Relative clauses
- 3.3.3. Infinitival clauses
- 3.3.4. A special case: clauses referring to a proposition
- 3.3.5. Adjectival phrases
- 3.3.6. Adverbial postmodification
- 3.4. Bibliographical notes
- 4 Projection of noun phrases III: binominal constructions
- Introduction
- 4.1. Binominal constructions without a preposition
- 4.2. Binominal constructions with a preposition
- 4.3. Bibliographical notes
- 5 Determiners: articles and pronouns
- Introduction
- 5.1. Articles
- 5.2. Pronouns
- 5.3. Bibliographical notes
- 6 Numerals and quantifiers
- 7 Pre-determiners
- Introduction
- 7.1. The universal quantifier al 'all' and its alternants
- 7.2. The pre-determiner heel 'all/whole'
- 7.3. A note on focus particles
- 7.4. Bibliographical notes
- 8 Syntactic uses of noun phrases
- Adjectives and Adjective Phrases
- 1 Characteristics and classification
- 2 Projection of adjective phrases I: Complementation
- 3 Projection of adjective phrases II: Modification
- 4 Projection of adjective phrases III: Comparison
- 5 Attributive use of the adjective phrase
- 6 Predicative use of the adjective phrase
- 7 The partitive genitive construction
- 8 Adverbial use of the adjective phrase
- 9 Participles and infinitives: their adjectival use
- 10 Special constructions
- Adpositions and adpositional phrases
- 1 Characteristics and classification
- Introduction
- 1.1. Characterization of the category adposition
- 1.2. A formal classification of adpositional phrases
- 1.3. A semantic classification of adpositional phrases
- 1.3.1. Spatial adpositions
- 1.3.2. Temporal adpositions
- 1.3.3. Non-spatial/temporal prepositions
- 1.4. Borderline cases
- 1.5. Bibliographical notes
- 2 Projection of adpositional phrases: Complementation
- 3 Projection of adpositional phrases: Modification
- 4 Syntactic uses of the adpositional phrase
- 5 R-pronominalization and R-words
- 1 Characteristics and classification
- Phonology
-
- General
- Phonology
- Segment inventory
- Phonotactics
- Phonological Processes
- Assimilation
- Vowel nasalization
- Syllabic sonorants
- Final devoicing
- Fake geminates
- Vowel hiatus resolution
- Vowel reduction introduction
- Schwa deletion
- Schwa insertion
- /r/-deletion
- d-insertion
- {s/z}-insertion
- t-deletion
- Intrusive stop formation
- Breaking
- Vowel shortening
- h-deletion
- Replacement of the glide w
- Word stress
- Clitics
- Allomorphy
- Orthography of Frisian
- Morphology
- Inflection
- Word formation
- Derivation
- Prefixation
- Infixation
- Suffixation
- Nominal suffixes
- Verbal suffixes
- Adjectival suffixes
- Adverbial suffixes
- Numeral suffixes
- Interjectional suffixes
- Onomastic suffixes
- Conversion
- Compositions
- Derivation
- Syntax
- Verbs and Verb Phrases
- Characteristics and classification
- Unergative and unaccusative subjects
- Evidentiality
- To-infinitival clauses
- Predication and noun incorporation
- Ellipsis
- Imperativus-pro-Infinitivo
- Expression of irrealis
- Embedded Verb Second
- Agreement
- Negation
- Nouns & Noun Phrases
- Classification
- Complementation
- Modification
- Partitive noun constructions
- Referential partitive constructions
- Partitive measure nouns
- Numeral partitive constructions
- Partitive question constructions
- Nominalised quantifiers
- Kind partitives
- Partitive predication with prepositions
- Bare nominal attributions
- Articles and names
- Pronouns
- Quantifiers and (pre)determiners
- Interrogative pronouns
- R-pronouns
- Syntactic uses
- Adjective Phrases
- Characteristics and classification
- Complementation
- Modification and degree quantification
- Comparison by degree
- Comparative
- Superlative
- Equative
- Attribution
- Agreement
- Attributive adjectives vs. prenominal elements
- Complex adjectives
- Noun ellipsis
- Co-occurring adjectives
- Predication
- Partitive adjective constructions
- Adverbial use
- Participles and infinitives
- Adposition Phrases
- Characteristics and classification
- Complementation
- Modification
- Intransitive adpositions
- Predication
- Preposition stranding
- Verbs and Verb Phrases
-
- General
- Morphology
- Morphology
- 1 Word formation
- 1.1 Compounding
- 1.1.1 Compounds and their heads
- 1.1.2 Special types of compounds
- 1.1.2.1 Affixoids
- 1.1.2.2 Coordinative compounds
- 1.1.2.3 Synthetic compounds and complex pseudo-participles
- 1.1.2.4 Reduplicative compounds
- 1.1.2.5 Phrase-based compounds
- 1.1.2.6 Elative compounds
- 1.1.2.7 Exocentric compounds
- 1.1.2.8 Linking elements
- 1.1.2.9 Separable Complex Verbs and Particle Verbs
- 1.1.2.10 Noun Incorporation Verbs
- 1.1.2.11 Gapping
- 1.2 Derivation
- 1.3 Minor patterns of word formation
- 1.1 Compounding
- 2 Inflection
- 1 Word formation
- Morphology
- Syntax
- Adjectives and adjective phrases (APs)
- 0 Introduction to the AP
- 1 Characteristics and classification of APs
- 2 Complementation of APs
- 3 Modification and degree quantification of APs
- 4 Comparison by comparative, superlative and equative
- 5 Attribution of APs
- 6 Predication of APs
- 7 The partitive adjective construction
- 8 Adverbial use of APs
- 9 Participles and infinitives as APs
- Nouns and Noun Phrases (NPs)
- 0 Introduction to the NP
- 1 Characteristics and Classification of NPs
- 2 Complementation of NPs
- 3 Modification of NPs
- 3.1 Modification of NP by Determiners and APs
- 3.2 Modification of NP by PP
- 3.3 Modification of NP by adverbial clauses
- 3.4 Modification of NP by possessors
- 3.5 Modification of NP by relative clauses
- 3.6 Modification of NP in a cleft construction
- 3.7 Free relative clauses and selected interrogative clauses
- 4 Partitive noun constructions and constructions related to them
- 4.1 The referential partitive construction
- 4.2 The partitive construction of abstract quantity
- 4.3 The numerical partitive construction
- 4.4 The partitive interrogative construction
- 4.5 Adjectival, nominal and nominalised partitive quantifiers
- 4.6 Kind partitives
- 4.7 Partitive predication with a preposition
- 4.8 Bare nominal attribution
- 5 Articles and names
- 6 Pronouns
- 7 Quantifiers, determiners and predeterminers
- 8 Interrogative pronouns
- 9 R-pronouns and the indefinite expletive
- 10 Syntactic functions of Noun Phrases
- Adpositions and Adpositional Phrases (PPs)
- 0 Introduction to the PP
- 1 Characteristics and classification of PPs
- 2 Complementation of PPs
- 3 Modification of PPs
- 4 Bare (intransitive) adpositions
- 5 Predication of PPs
- 6 Form and distribution of adpositions with respect to staticity and construction type
- 7 Adpositional complements and adverbials
- Verbs and Verb Phrases (VPs)
- 0 Introduction to the VP in Saterland Frisian
- 1 Characteristics and classification of verbs
- 2 Unergative and unaccusative subjects and the auxiliary of the perfect
- 3 Evidentiality in relation to perception and epistemicity
- 4 Types of to-infinitival constituents
- 5 Predication
- 5.1 The auxiliary of being and its selection restrictions
- 5.2 The auxiliary of going and its selection restrictions
- 5.3 The auxiliary of continuation and its selection restrictions
- 5.4 The auxiliary of coming and its selection restrictions
- 5.5 Modal auxiliaries and their selection restrictions
- 5.6 Auxiliaries of body posture and aspect and their selection restrictions
- 5.7 Transitive verbs of predication
- 5.8 The auxiliary of doing used as a semantically empty finite auxiliary
- 5.9 Supplementive predication
- 6 The verbal paradigm, irregularity and suppletion
- 7 Verb Second and the word order in main and embedded clauses
- 8 Various aspects of clause structure
- Adjectives and adjective phrases (APs)
-
- General
- Phonology
- Afrikaans phonology
- Segment inventory
- Overview of Afrikaans vowels
- The diphthongised long vowels /e/, /ø/ and /o/
- The unrounded mid-front vowel /ɛ/
- The unrounded low-central vowel /ɑ/
- The unrounded low-central vowel /a/
- The rounded mid-high back vowel /ɔ/
- The rounded high back vowel /u/
- The rounded and unrounded high front vowels /i/ and /y/
- The unrounded and rounded central vowels /ə/ and /œ/
- The diphthongs /əi/, /œy/ and /œu/
- Overview of Afrikaans consonants
- The bilabial plosives /p/ and /b/
- The alveolar plosives /t/ and /d/
- The velar plosives /k/ and /g/
- The bilabial nasal /m/
- The alveolar nasal /n/
- The velar nasal /ŋ/
- The trill /r/
- The lateral liquid /l/
- The alveolar fricative /s/
- The velar fricative /x/
- The labiodental fricatives /f/ and /v/
- The approximants /ɦ/, /j/ and /ʋ/
- Overview of Afrikaans vowels
- Word stress
- The phonetic properties of stress
- Primary stress on monomorphemic words in Afrikaans
- Background to primary stress in monomorphemes in Afrikaans
- Overview of the Main Stress Rule of Afrikaans
- The short vowels of Afrikaans
- Long vowels in monomorphemes
- Primary stress on diphthongs in monomorphemes
- Exceptions
- Stress shifts in place names
- Stress shift towards word-final position
- Stress pattern of reduplications
- Phonological processes
- Vowel related processes
- Consonant related processes
- Homorganic glide insertion
- Phonology-morphology interface
- Phonotactics
- Morphology
- Syntax
- Afrikaans syntax
- Nouns and noun phrases
- Characteristics of the NP
- Classification of nouns
- Complementation of NPs
- Modification of NPs
- Binominal and partitive constructions
- Referential partitive constructions
- Partitive measure nouns
- Numeral partitive constructions
- Partitive question constructions
- Partitive constructions with nominalised quantifiers
- Partitive predication with prepositions
- Binominal name constructions
- Binominal genitive constructions
- Bare nominal attribution
- Articles and names
- Pronouns
- Quantifiers, determiners and predeterminers
- Syntactic uses of the noun phrase
- Adjectives and adjective phrases
- Characteristics and classification of the AP
- Complementation of APs
- Modification and Degree Quantification of APs
- Comparison by comparative, superlative and equative degree
- Attribution of APs
- Predication of APs
- The partitive adjective construction
- Adverbial use of APs
- Participles and infinitives as adjectives
- Verbs and verb phrases
- Characterisation and classification
- Argument structure
- Verb frame alternations
- Complements of non-main verbs
- Verb clusters
- Complement clauses
- Adverbial modification
- Word order in the clause: Introduction
- Word order in the clause: position of the finite Verb
- Word order in the clause: Clause-initial position
- Word order in the clause: Extraposition and right-dislocation in the postverbal field
- Word order in the middle field
- Emphatic constructions
- Adpositions and adposition phrases
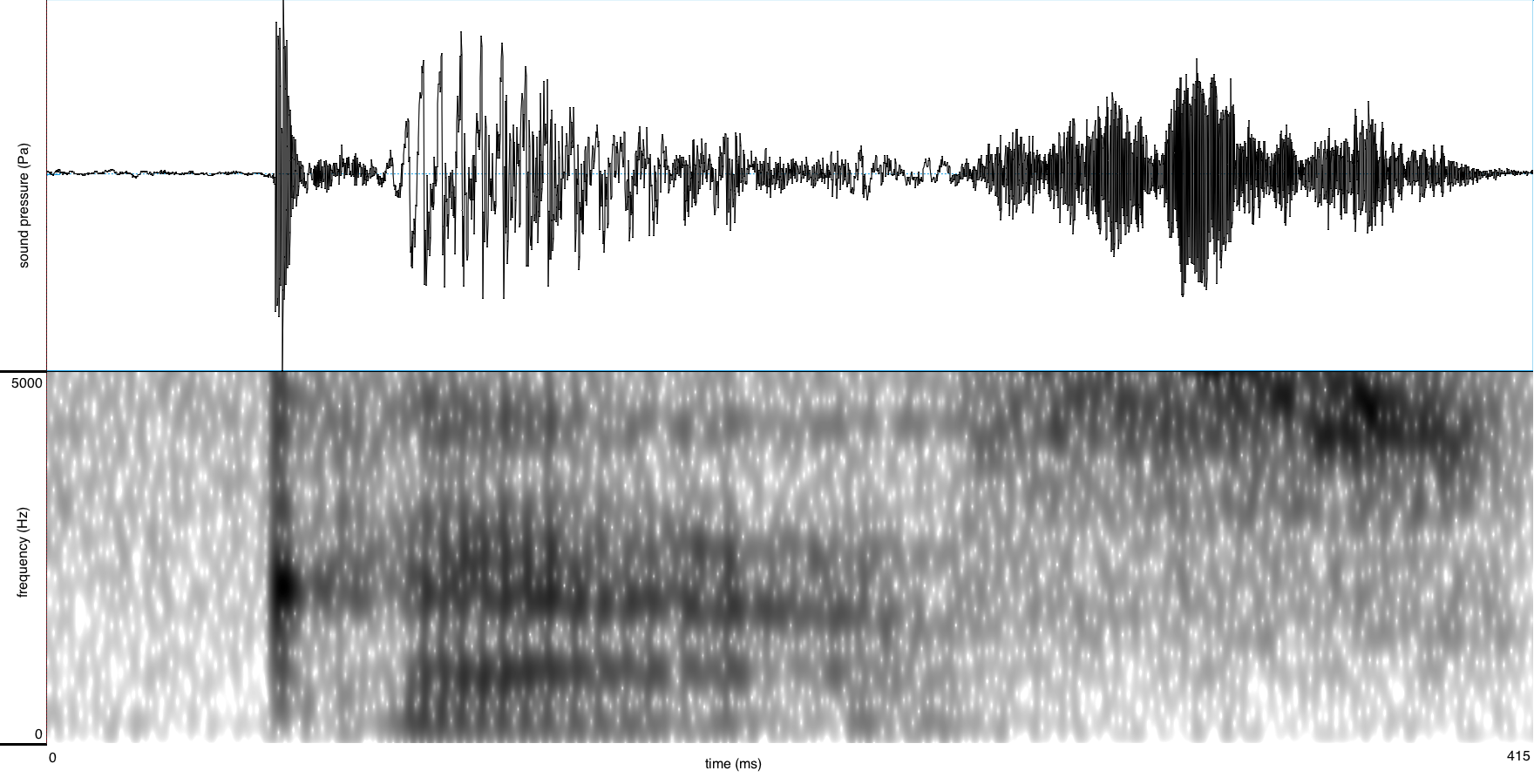
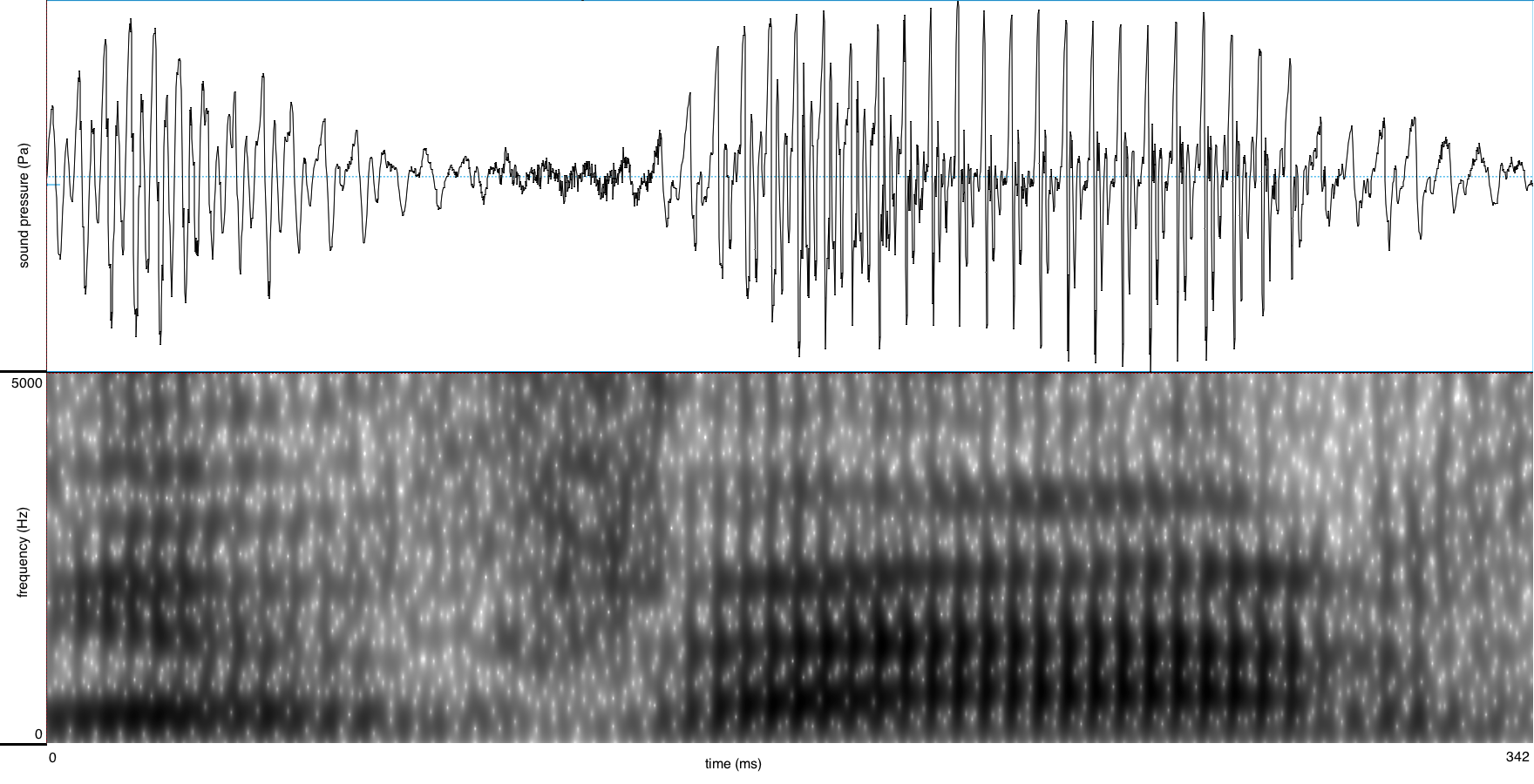
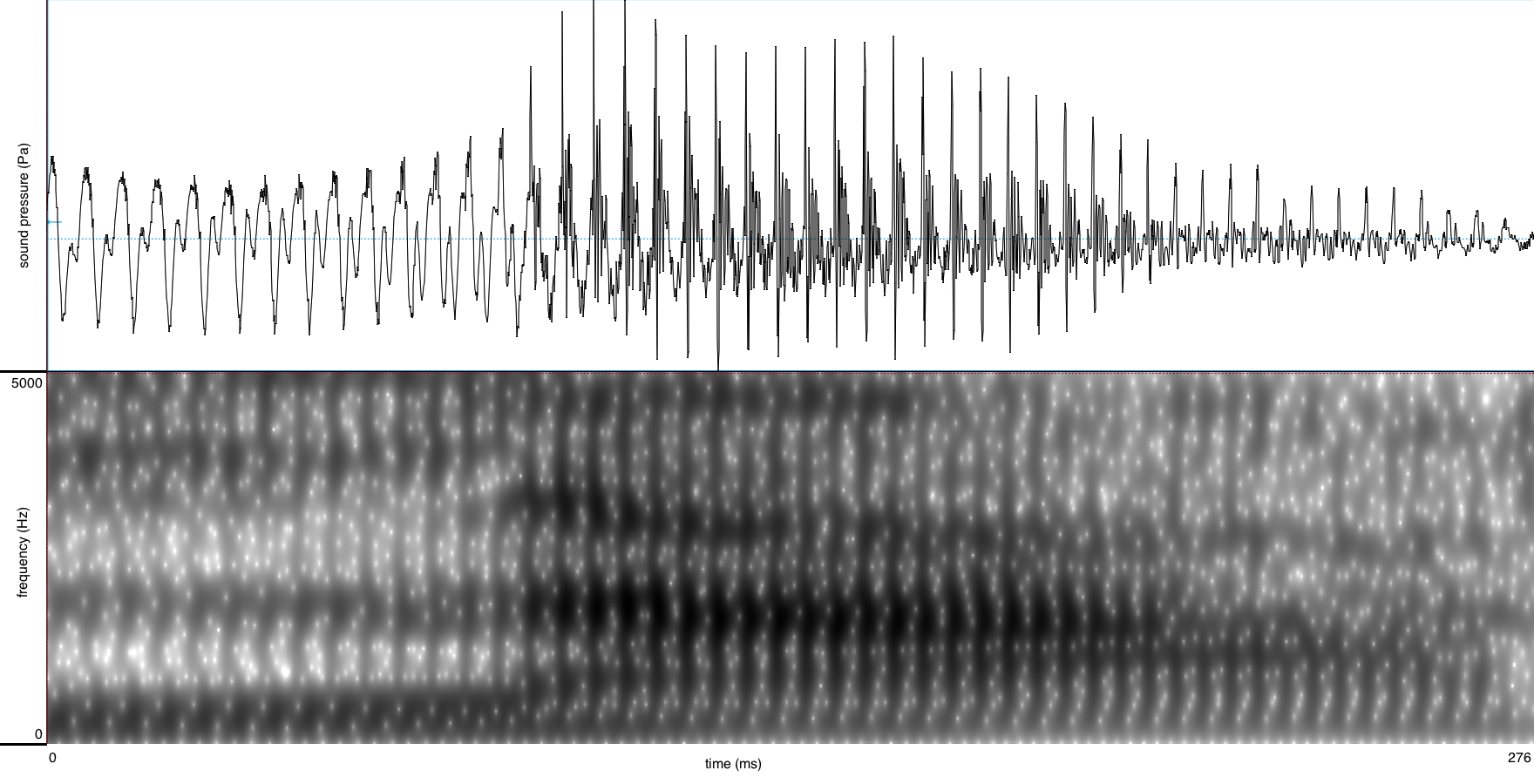
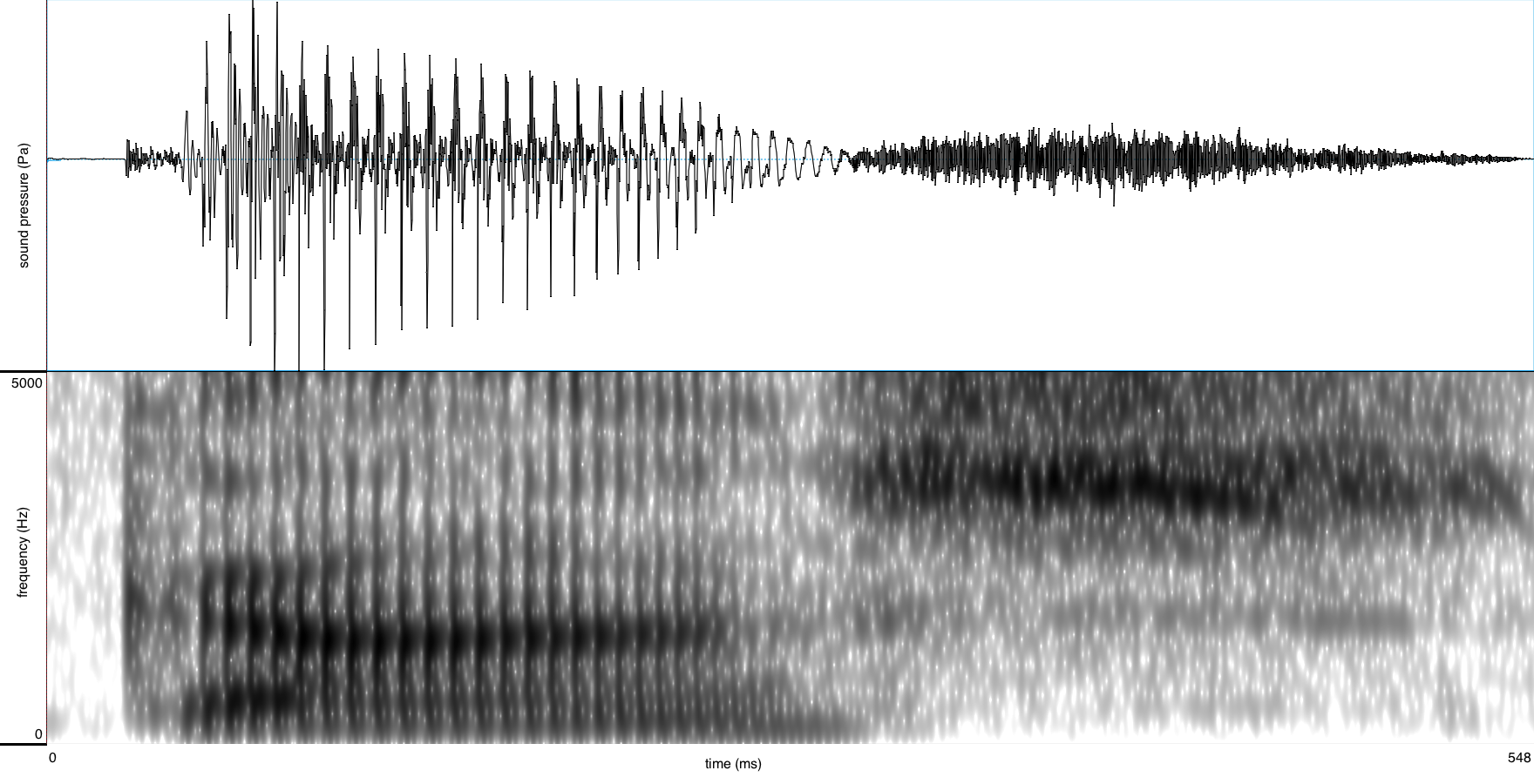
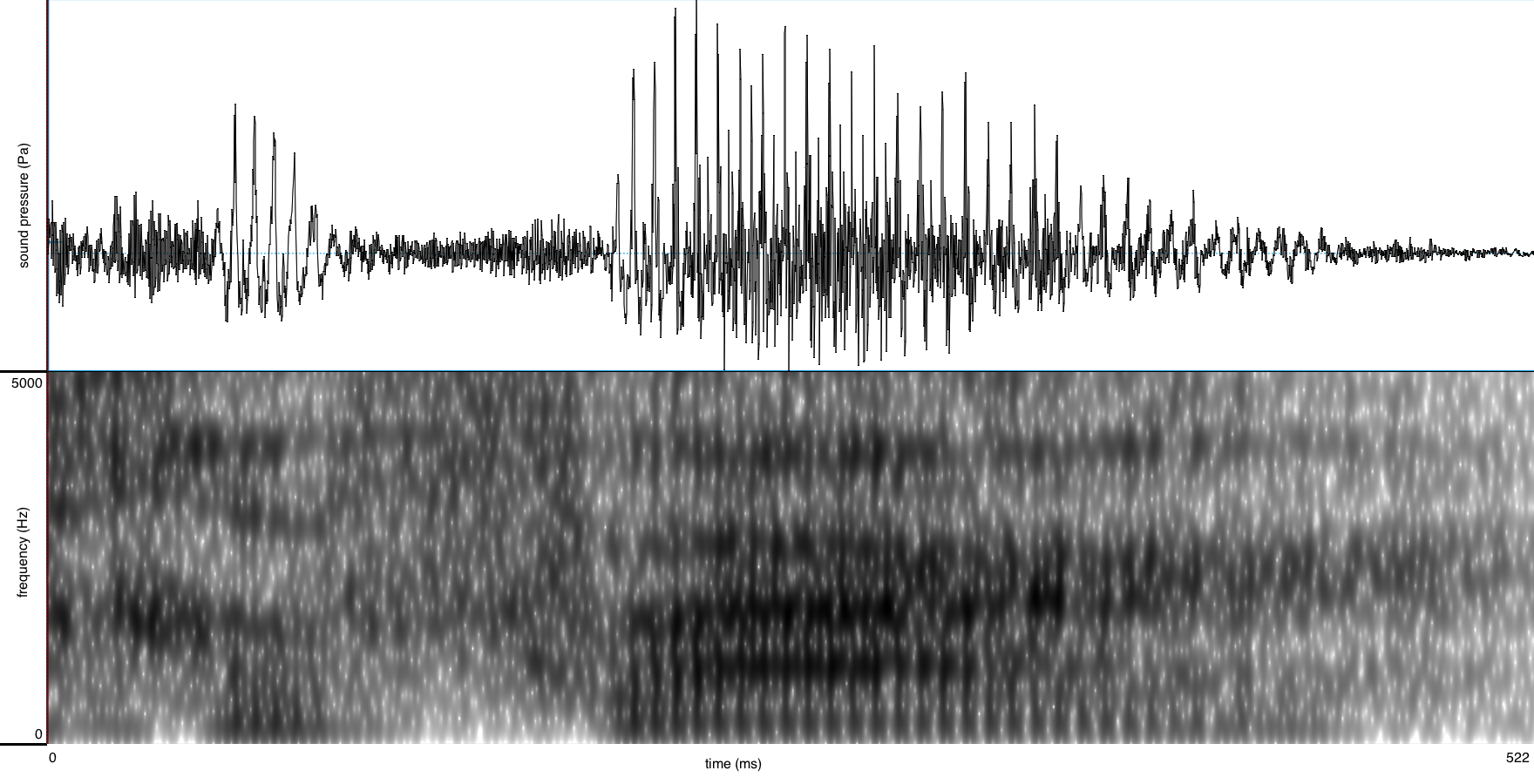
The unrounded low front-central A-class vowel /a/ is found in words such as:
It is spelled with a single letter <a> in open syllables; this letter is doubled (<aa>) in closed syllables.
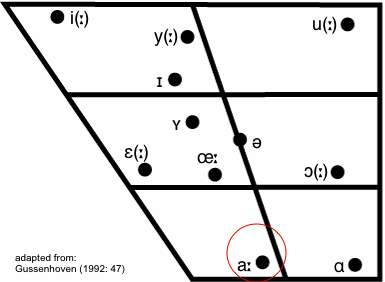
Figure 1(cf. Gussenhoven 1992) depicts the (Dutch) vowel's position within the vowel chart.
Formant values vary with the type of speech, gender of the speaker, and speech community (the Netherlands or Flanders). Below are some reported average F1/F2 values.
| F1 | mixed | female | male |
| Netherlands | 801 | 986 | 795 |
| 771 | 912 | 738 | |
| 670 | |||
| Flanders | 826 | 868 | 717 |
| 807 |
| F2 | mixed | female | male |
| Netherlands | 1498 | 1443 | 1301 |
| 1509 | 1572 | 1409 | |
| 1425 | |||
| Flanders | 1506 | 1640 | 1429 |
| 1511 |
| Canada | [kanada] | / | [kɑnadɑ] | / | [kɑnɑda] | / | [kɑnɑdɑ] | / | [*kanadɑ] | / | [*kanɑdɑ] |
This variation is at least partially regional and has not been seriously studied; it seems to us for instance, that [ɑ] at the end of the word is only found in Flanders. What exactly determines the reason why some a [a]’s can be realized as [ɑ]'s or vice versa, whereas others cannot, is not clear. Also otherwise, the two vowels seem sometimes to change position. For instance, the generalization that intervocalic fricatives are voiced after a tautomorphemic A-class vowel and voiceless after a B-class vowel has exceptions exactly with this pair:
- 2004An acoustic description of the vowels of Northern and Southern Standard DutchJournal of the Acoustical Society of America1161729--1738
- 2004An acoustic description of the vowels of Northern and Southern Standard DutchJournal of the Acoustical Society of America1161729--1738
- 2003The Phonetics of English and DutchLeidenE.J. Brill
- 2003The Phonetics of English and DutchLeidenE.J. Brill
- 2003The Phonetics of English and DutchLeidenE.J. Brill
- 1937Phonetiek van het NederlandsHaarlemDe Erven F. Bohn N.V.
- 1992DutchJournal of the International Phonetic Association2245-47
- 1993The Dutch foot and the chanted callJournal of Linguistics2937-63
- 2009On Variation and Change in Diphthongs and Long Vowels of Spoken DutchUniversity of AmsterdamThesis


.png)