- Dutch
- Frisian
- Saterfrisian
- Afrikaans
-
- Phonology
- Segment inventory
- Phonotactics
- Phonological processes
- Phonology-morphology interface
- Word stress
- Primary stress in simplex words
- Monomorphemic words
- Diachronic aspects
- Generalizations on stress placement
- Default penultimate stress
- Lexical stress
- The closed penult restriction
- Final closed syllables
- The diphthong restriction
- Superheavy syllables (SHS)
- The three-syllable window
- Segmental restrictions
- Phonetic correlates
- Stress shifts in loanwords
- Quantity-sensitivity
- Secondary stress
- Vowel reduction in unstressed syllables
- Stress in complex words
- Primary stress in simplex words
- Accent & intonation
- Clitics
- Spelling
- Morphology
- Word formation
- Compounding
- Nominal compounds
- Verbal compounds
- Adjectival compounds
- Affixoids
- Coordinative compounds
- Synthetic compounds
- Reduplicative compounds
- Phrase-based compounds
- Elative compounds
- Exocentric compounds
- Linking elements
- Separable complex verbs (SCVs)
- Gapping of complex words
- Particle verbs
- Copulative compounds
- Derivation
- Numerals
- Derivation: inputs and input restrictions
- The meaning of affixes
- Non-native morphology
- Cohering and non-cohering affixes
- Prefixation
- Suffixation
- Nominal suffixation: person nouns
- Conversion
- Pseudo-participles
- Bound forms
- Nouns
- Nominal prefixes
- Nominal suffixes
- -aal and -eel
- -aar
- -aard
- -aat
- -air
- -aris
- -ast
- Diminutives
- -dom
- -een
- -ees
- -el (nominal)
- -elaar
- -enis
- -er (nominal)
- -erd
- -erik
- -es
- -eur
- -euse
- ge...te
- -heid
- -iaan, -aan
- -ief
- -iek
- -ier
- -ier (French)
- -ière
- -iet
- -igheid
- -ij and allomorphs
- -ijn
- -in
- -ing
- -isme
- -ist
- -iteit
- -ling
- -oir
- -oot
- -rice
- -schap
- -schap (de)
- -schap (het)
- -sel
- -st
- -ster
- -t
- -tal
- -te
- -voud
- Verbs
- Adjectives
- Adverbs
- Univerbation
- Neo-classical word formation
- Construction-dependent morphology
- Morphological productivity
- Compounding
- Inflection
- Inflection and derivation
- Allomorphy
- The interface between phonology and morphology
- Word formation
- Syntax
- Preface and acknowledgements
- Verbs and Verb Phrases
- 1 Characterization and classification
- 2 Projection of verb phrases I:Argument structure
- 3 Projection of verb phrases II:Verb frame alternations
- Introduction
- 3.1. Main types
- 3.2. Alternations involving the external argument
- 3.3. Alternations of noun phrases and PPs
- 3.3.1. Dative/PP alternations (dative shift)
- 3.3.1.1. Dative alternation with aan-phrases (recipients)
- 3.3.1.2. Dative alternation with naar-phrases (goals)
- 3.3.1.3. Dative alternation with van-phrases (sources)
- 3.3.1.4. Dative alternation with bij-phrases (possessors)
- 3.3.1.5. Dative alternation with voor-phrases (benefactives)
- 3.3.1.6. Conclusion
- 3.3.1.7. Bibliographical notes
- 3.3.2. Accusative/PP alternations
- 3.3.3. Nominative/PP alternations
- 3.3.1. Dative/PP alternations (dative shift)
- 3.4. Some apparent cases of verb frame alternation
- 3.5. Bibliographical notes
- 4 Projection of verb phrases IIIa:Selection of clauses/verb phrases
- 5 Projection of verb phrases IIIb:Argument and complementive clauses
- Introduction
- 5.1. Finite argument clauses
- 5.2. Infinitival argument clauses
- 5.3. Complementive clauses
- 6 Projection of verb phrases IIIc:Complements of non-main verbs
- 7 Projection of verb phrases IIId:Verb clusters
- 8 Projection of verb phrases IV: Adverbial modification
- 9 Word order in the clause I:General introduction
- 10 Word order in the clause II:Position of the finite verb (verb-first/second)
- 11 Word order in the clause III:Clause-initial position (wh-movement)
- Introduction
- 11.1. The formation of V1- and V2-clauses
- 11.2. Clause-initial position remains (phonetically) empty
- 11.3. Clause-initial position is filled
- 12 Word order in the clause IV:Postverbal field (extraposition)
- 13 Word order in the clause V: Middle field (scrambling)
- 14 Main-clause external elements
- Nouns and Noun Phrases
- 1 Characterization and classification
- 2 Projection of noun phrases I: complementation
- Introduction
- 2.1. General observations
- 2.2. Prepositional and nominal complements
- 2.3. Clausal complements
- 2.4. Bibliographical notes
- 3 Projection of noun phrases II: modification
- Introduction
- 3.1. Restrictive and non-restrictive modifiers
- 3.2. Premodification
- 3.3. Postmodification
- 3.3.1. Adpositional phrases
- 3.3.2. Relative clauses
- 3.3.3. Infinitival clauses
- 3.3.4. A special case: clauses referring to a proposition
- 3.3.5. Adjectival phrases
- 3.3.6. Adverbial postmodification
- 3.4. Bibliographical notes
- 4 Projection of noun phrases III: binominal constructions
- Introduction
- 4.1. Binominal constructions without a preposition
- 4.2. Binominal constructions with a preposition
- 4.3. Bibliographical notes
- 5 Determiners: articles and pronouns
- Introduction
- 5.1. Articles
- 5.2. Pronouns
- 5.3. Bibliographical notes
- 6 Numerals and quantifiers
- 7 Pre-determiners
- Introduction
- 7.1. The universal quantifier al 'all' and its alternants
- 7.2. The pre-determiner heel 'all/whole'
- 7.3. A note on focus particles
- 7.4. Bibliographical notes
- 8 Syntactic uses of noun phrases
- Adjectives and Adjective Phrases
- 1 Characteristics and classification
- 2 Projection of adjective phrases I: Complementation
- 3 Projection of adjective phrases II: Modification
- 4 Projection of adjective phrases III: Comparison
- 5 Attributive use of the adjective phrase
- 6 Predicative use of the adjective phrase
- 7 The partitive genitive construction
- 8 Adverbial use of the adjective phrase
- 9 Participles and infinitives: their adjectival use
- 10 Special constructions
- Adpositions and adpositional phrases
- 1 Characteristics and classification
- Introduction
- 1.1. Characterization of the category adposition
- 1.2. A formal classification of adpositional phrases
- 1.3. A semantic classification of adpositional phrases
- 1.3.1. Spatial adpositions
- 1.3.2. Temporal adpositions
- 1.3.3. Non-spatial/temporal prepositions
- 1.4. Borderline cases
- 1.5. Bibliographical notes
- 2 Projection of adpositional phrases: Complementation
- 3 Projection of adpositional phrases: Modification
- 4 Syntactic uses of the adpositional phrase
- 5 R-pronominalization and R-words
- 1 Characteristics and classification
- Phonology
-
- General
- Phonology
- Segment inventory
- Phonotactics
- Phonological Processes
- Assimilation
- Vowel nasalization
- Syllabic sonorants
- Final devoicing
- Fake geminates
- Vowel hiatus resolution
- Vowel reduction introduction
- Schwa deletion
- Schwa insertion
- /r/-deletion
- d-insertion
- {s/z}-insertion
- t-deletion
- Intrusive stop formation
- Breaking
- Vowel shortening
- h-deletion
- Replacement of the glide w
- Word stress
- Clitics
- Allomorphy
- Orthography of Frisian
- Morphology
- Inflection
- Word formation
- Derivation
- Prefixation
- Infixation
- Suffixation
- Nominal suffixes
- Verbal suffixes
- Adjectival suffixes
- Adverbial suffixes
- Numeral suffixes
- Interjectional suffixes
- Onomastic suffixes
- Conversion
- Compositions
- Derivation
- Syntax
- Verbs and Verb Phrases
- Characteristics and classification
- Unergative and unaccusative subjects
- Evidentiality
- To-infinitival clauses
- Predication and noun incorporation
- Ellipsis
- Imperativus-pro-Infinitivo
- Expression of irrealis
- Embedded Verb Second
- Agreement
- Negation
- Nouns & Noun Phrases
- Classification
- Complementation
- Modification
- Partitive noun constructions
- Referential partitive constructions
- Partitive measure nouns
- Numeral partitive constructions
- Partitive question constructions
- Nominalised quantifiers
- Kind partitives
- Partitive predication with prepositions
- Bare nominal attributions
- Articles and names
- Pronouns
- Quantifiers and (pre)determiners
- Interrogative pronouns
- R-pronouns
- Syntactic uses
- Adjective Phrases
- Characteristics and classification
- Complementation
- Modification and degree quantification
- Comparison by degree
- Comparative
- Superlative
- Equative
- Attribution
- Agreement
- Attributive adjectives vs. prenominal elements
- Complex adjectives
- Noun ellipsis
- Co-occurring adjectives
- Predication
- Partitive adjective constructions
- Adverbial use
- Participles and infinitives
- Adposition Phrases
- Characteristics and classification
- Complementation
- Modification
- Intransitive adpositions
- Predication
- Preposition stranding
- Verbs and Verb Phrases
-
- General
- Morphology
- Morphology
- 1 Word formation
- 1.1 Compounding
- 1.1.1 Compounds and their heads
- 1.1.2 Special types of compounds
- 1.1.2.1 Affixoids
- 1.1.2.2 Coordinative compounds
- 1.1.2.3 Synthetic compounds and complex pseudo-participles
- 1.1.2.4 Reduplicative compounds
- 1.1.2.5 Phrase-based compounds
- 1.1.2.6 Elative compounds
- 1.1.2.7 Exocentric compounds
- 1.1.2.8 Linking elements
- 1.1.2.9 Separable Complex Verbs and Particle Verbs
- 1.1.2.10 Noun Incorporation Verbs
- 1.1.2.11 Gapping
- 1.2 Derivation
- 1.3 Minor patterns of word formation
- 1.1 Compounding
- 2 Inflection
- 1 Word formation
- Morphology
- Syntax
- Adjectives and adjective phrases (APs)
- 0 Introduction to the AP
- 1 Characteristics and classification of APs
- 2 Complementation of APs
- 3 Modification and degree quantification of APs
- 4 Comparison by comparative, superlative and equative
- 5 Attribution of APs
- 6 Predication of APs
- 7 The partitive adjective construction
- 8 Adverbial use of APs
- 9 Participles and infinitives as APs
- Nouns and Noun Phrases (NPs)
- 0 Introduction to the NP
- 1 Characteristics and Classification of NPs
- 2 Complementation of NPs
- 3 Modification of NPs
- 3.1 Modification of NP by Determiners and APs
- 3.2 Modification of NP by PP
- 3.3 Modification of NP by adverbial clauses
- 3.4 Modification of NP by possessors
- 3.5 Modification of NP by relative clauses
- 3.6 Modification of NP in a cleft construction
- 3.7 Free relative clauses and selected interrogative clauses
- 4 Partitive noun constructions and constructions related to them
- 4.1 The referential partitive construction
- 4.2 The partitive construction of abstract quantity
- 4.3 The numerical partitive construction
- 4.4 The partitive interrogative construction
- 4.5 Adjectival, nominal and nominalised partitive quantifiers
- 4.6 Kind partitives
- 4.7 Partitive predication with a preposition
- 4.8 Bare nominal attribution
- 5 Articles and names
- 6 Pronouns
- 7 Quantifiers, determiners and predeterminers
- 8 Interrogative pronouns
- 9 R-pronouns and the indefinite expletive
- 10 Syntactic functions of Noun Phrases
- Adpositions and Adpositional Phrases (PPs)
- 0 Introduction to the PP
- 1 Characteristics and classification of PPs
- 2 Complementation of PPs
- 3 Modification of PPs
- 4 Bare (intransitive) adpositions
- 5 Predication of PPs
- 6 Form and distribution of adpositions with respect to staticity and construction type
- 7 Adpositional complements and adverbials
- Verbs and Verb Phrases (VPs)
- 0 Introduction to the VP in Saterland Frisian
- 1 Characteristics and classification of verbs
- 2 Unergative and unaccusative subjects and the auxiliary of the perfect
- 3 Evidentiality in relation to perception and epistemicity
- 4 Types of to-infinitival constituents
- 5 Predication
- 5.1 The auxiliary of being and its selection restrictions
- 5.2 The auxiliary of going and its selection restrictions
- 5.3 The auxiliary of continuation and its selection restrictions
- 5.4 The auxiliary of coming and its selection restrictions
- 5.5 Modal auxiliaries and their selection restrictions
- 5.6 Auxiliaries of body posture and aspect and their selection restrictions
- 5.7 Transitive verbs of predication
- 5.8 The auxiliary of doing used as a semantically empty finite auxiliary
- 5.9 Supplementive predication
- 6 The verbal paradigm, irregularity and suppletion
- 7 Verb Second and the word order in main and embedded clauses
- 8 Various aspects of clause structure
- Adjectives and adjective phrases (APs)
-
- General
- Phonology
- Afrikaans phonology
- Segment inventory
- Overview of Afrikaans vowels
- The diphthongised long vowels /e/, /ø/ and /o/
- The unrounded mid-front vowel /ɛ/
- The unrounded low-central vowel /ɑ/
- The unrounded low-central vowel /a/
- The rounded mid-high back vowel /ɔ/
- The rounded high back vowel /u/
- The rounded and unrounded high front vowels /i/ and /y/
- The unrounded and rounded central vowels /ə/ and /œ/
- The diphthongs /əi/, /œy/ and /œu/
- Overview of Afrikaans consonants
- The bilabial plosives /p/ and /b/
- The alveolar plosives /t/ and /d/
- The velar plosives /k/ and /g/
- The bilabial nasal /m/
- The alveolar nasal /n/
- The velar nasal /ŋ/
- The trill /r/
- The lateral liquid /l/
- The alveolar fricative /s/
- The velar fricative /x/
- The labiodental fricatives /f/ and /v/
- The approximants /ɦ/, /j/ and /ʋ/
- Overview of Afrikaans vowels
- Word stress
- The phonetic properties of stress
- Primary stress on monomorphemic words in Afrikaans
- Background to primary stress in monomorphemes in Afrikaans
- Overview of the Main Stress Rule of Afrikaans
- The short vowels of Afrikaans
- Long vowels in monomorphemes
- Primary stress on diphthongs in monomorphemes
- Exceptions
- Stress shifts in place names
- Stress shift towards word-final position
- Stress pattern of reduplications
- Phonological processes
- Vowel related processes
- Consonant related processes
- Homorganic glide insertion
- Phonology-morphology interface
- Phonotactics
- Morphology
- Syntax
- Afrikaans syntax
- Nouns and noun phrases
- Characteristics of the NP
- Classification of nouns
- Complementation of NPs
- Modification of NPs
- Binominal and partitive constructions
- Referential partitive constructions
- Partitive measure nouns
- Numeral partitive constructions
- Partitive question constructions
- Partitive constructions with nominalised quantifiers
- Partitive predication with prepositions
- Binominal name constructions
- Binominal genitive constructions
- Bare nominal attribution
- Articles and names
- Pronouns
- Quantifiers, determiners and predeterminers
- Syntactic uses of the noun phrase
- Adjectives and adjective phrases
- Characteristics and classification of the AP
- Complementation of APs
- Modification and Degree Quantification of APs
- Comparison by comparative, superlative and equative degree
- Attribution of APs
- Predication of APs
- The partitive adjective construction
- Adverbial use of APs
- Participles and infinitives as adjectives
- Verbs and verb phrases
- Characterisation and classification
- Argument structure
- Verb frame alternations
- Complements of non-main verbs
- Verb clusters
- Complement clauses
- Adverbial modification
- Word order in the clause: Introduction
- Word order in the clause: position of the finite Verb
- Word order in the clause: Clause-initial position
- Word order in the clause: Extraposition and right-dislocation in the postverbal field
- Word order in the middle field
- Emphatic constructions
- Adpositions and adposition phrases
Phonological processes (rules) mediate between underlying, basic phonological forms (constituted by strings of phonemes) on the one hand and surface, phonetic forms (constituted by strings of phones i.e. allophones of phonemes) on the other. In essence, such mediation implies that rules are optional. In theory then, obligatory rules do not exist. This section deals with the most important phonological processes of Afrikaans.
The overall goal of the Taalportaal project is the construction of a comprehensive and authoritative scientific grammar of Dutch, Frisian and Afrikaans. At the same time, the aim is not to operate strictly within a specific theoretical framework such as, for example, in the case of phonology, generative or optimality phonology. At the same time, the description of the phonology of Afrikaans (or any language for that matter) cannot be completely untheoretical and, in what follows, applicable reference is made to all available relevant literature on a specific topic, regardless of its theoretical heritage.
As an orientation with respect to all topics concerning the most important Afrikaans phonological processes, the following reference list should be consulted:
(Donaldson, 1993; Le Roux and Pienaar, 1927; Combrink and De Stadler, 1987; De Villiers and Ponelis, 1992; Wissing, 1982; Wissing, 1991; Wissing, 1990; Wissing, 1990; Wissing, 1992; Wissing, 1994; Wissing, 2005; Coetzee 2014; Wissing, 2006; Wissing, 2010; Wissing, 2011; Wissing, 2014; Wissing, 1995; Wissing, 2011; Wissing and Coetzee, 1996; Wissing and Du Plessis, 1992; Wissing and Van Dijkhorst, 2006; Wissing, 1978; Wissing, 1987; Wissing, 1989; Lubbe and Zonneveld, 1996; Ernestus, 2000; Schuppler et al. 2011; Zonneveld, 1978; De Stadler, 1989; Coetzee, 1977; Coetzee, 1990; Coetzee, 1992; Coetzee, 1990; Coetzee, 1991; Wissing, 2017; Carstens and Bosman, 2017).
As a demonstration of the nature and functioning of a phonological process, consider the following:
The coda consonant /n/ of the first syllable ( sin-) of the words sintaksis [səntɑksəs] syntax and sinchronies [səŋkronis] synchronic is realised differently, triggered by the place of articulation of the following consonant viz. alveolar in the first instance and velar in the second. In both cases, one can assume that these are two phonetic manifestations of the same basic phoneme viz. /n/. In order to express the different phonetic alternations or realizations found in examples like these, certain theoretical frameworks, notably forms of generative phonology, maintain that surface phonetic representations are derived by means of phonological rules from underlying representations (see figure below). As such, /n/ may be pronounced as [n], or, alternatively, as [ŋ] or [m] in derivations with in- in respectively intrap [əntrɑp] to step in, inkɔm [əŋkɔm] to come in and inpɑs [əmpɑs] to fit in. The same applies to prefixes like on-, aan- and van-. It also occurs frequently across word boundaries in sentence context.
This type of alternation, called homorganic nasal assimilation, affects consonant realizations. Similarly, vowels can be produced in more than one way, as in the case of their reduction, or in instances of unrounding. The vowel [ɑ] in kanon canon frequently reduces to schwa in [kənɔn]; the vowel [y] in nuus [nys] news is commonly unrounded, rendering [nis]. Other commonly observed processes that affect pronunciation are the raising, lowering and centralising of vowels, to be dealt with in other topics (see the index at the bottom of this page).
The following figure depicts the above-mentioned example of nasal assimilation.
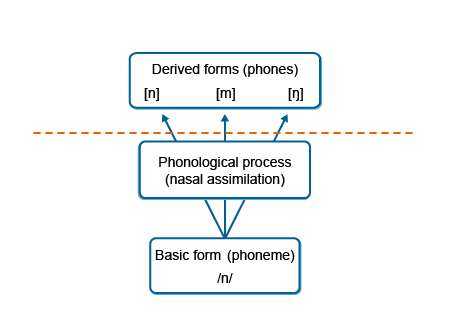
- The red broken line indicates the division between underlying (abstract) and surface (directly observable) structures. Accordingly, phonological processes (here nasal assimilation) are also underlying, representing a largely unconscious form of knowlegde – in a number of theoretical frameworks these processes are expressed in terms of phonological rules which are posited as being found in the mind/brain of a person who speaks a particular language.
- The phoneme /n/ is here seen as the underlying representation of the three allophones viz. the surface forms [n], [ŋ] and [m]. They correspond with respect to their place of articulation (i.e. are homorganic) to the respective following consonant (alveolar, velar, bilabial).
Some rules are more likely to be applied than others. To a large extent, the degree to which rules apply (expressed in terms of Rule Application Probability; RAP) depends on factors such as the nature of the speech style (casual rather than formal) or speech rate (rapid rather than slow). Labov (1972) defines casual speech, in contrast to formal speech, as everyday speech used in informal situations in which no special attention is paid to expression. Generally, casual speech is produced at a faster tempo than formal spoken language. High-speech tempo generally induces higher RAPs (Wissing and Van Dijkhorst, 2006). Other factors of importance for RAP are mentioned below. Consider the following examples regarding RAP, which varies on an index of 0.0 to 1.0: except in the case of extremely careful (slow) speech, identical consonants adjacent to each other are practically always realised as a single segment (thus RAP = 1.0), as explained further in Degemination. An example of the product of the Degemination Rule (sometimes called "amalgamation of identical consonants"), would be dis seker /dəs sekər/ pronounced as [dəsiəkər]. A rule like /d/-deletion, on the other hand, is not likely to be applied in careful speech in cases such as kinders /kəndərs/ [kəndərs], but most probably will appear in casual speech, resulting in [kənərs]. This means that the RAP of /d/-deletion will lie somewhere between 0.0 and 1.0. (cf. d-deletion).
The occurrence of the pronunciation of the demonstrative pronoun daardie /dardi/ that one in formal style [dardi] versus casual speech [dai] illustrates the impact of speech style perfectly. Speech rate could very well be a decisive factor: the RAP for [dai] will most probably be even higher in casual speech used at a high speaking tempo.
Several data sets, comprising sound files and associated phonetic transcriptions of a diverse kind, were available for inspection and analysis, namely a) recordings since 2001, over a time span of more than six years, of news broadcasts read by a number of prominent radio presenters of RSG (Radio Sonder Grense, a nationwide Afrikaans radio station), containing nearly ten hours of speech; and b) two sets of readings (SALAR = South African Language Resources, collected as part of a joint research project with the University of Ghent, Belgium; 2001 – 2003) of a diverse collection of prose by 129 Afrikaans-speaking persons of different ages, totalling about X hours of sound. For (b), each person had to read a passage of about 100 words twice: first at a normal tempo (RAN = Read Afrikaans Normal), and then at a fast tempo (RAF = Read Afrikaans Fast). The RSG recordings are taken as representative of Standard Afrikaans, read in a formal mode. Note, however, that the readers were all professionally skilled and trained to read in a relaxed way that could be considered approaching a casual speaking style, not very unlike what might be considered General Afrikaans (see a discussion of the concepts Standard Afrikaans, General Afrikaans, formal and casual speech here).
The probability of application of phonological rules is also sensitive to a number of factors other than speech style and rate. Some of the most well-known factors are listed below (1 – 6 are broadly linguistic categories; the rest relate to sociolinguistic characteristics):
- Casual speech: Speech styles can be formal, semi-formal or informal. Formal speech typically is that found in radio and television news broadcasts, sermons, public speeches and the like. Usually, though not without exception, such speakers may be expected to be "standard" speakers of Afrikaans. The same persons are likely to speak in a less formal way – semi-formal of informal – in less formal situations; as such, their speech in these contexts is broadly characterisable as casual. Casual speech correlates closely with ease of articulation (Ernestus, 2000). Labov's (1972) definition of casual speech, paraphrased above, is adopted here.
- Standard Afrikaans: Standard Afrikaans is currently mainly used in public contexts. Most studies on Afrikaans phonology are devoted to Standard Afrikaans. Due to the availability of studies being primarily restricted to this variety, in the respective themes on phonological processes (see below) it will also be the main variety described. The description of General Afrikaans (see 1.2) will, however, build on this.
- General Afrikaans: We equate this variety with casual Afrikaans as described above. Casual variants of many languages other than English, Dutch and German are still completely unexplored (Ernestus, 2000). This includes Afrikaans and, thus, the descriptions presented here are based on personal observation, as well as on an electronic collection of Afrikaans read at a fast rate. This data set, SALAR, is comprised of 129 different text passages of, on average, 100 words each and read by 129 different Afrikaans-speaking persons of both genders, young and old.
- Grammatical category: function words often surface in highly reduced form. This may be ascribed also to the fact that such words have a very high frequency usage (see 6) and, consequently, speakers are familiar with such words (5). That is not to say, however, that words other than this type are not also susceptible to the effect of phonological processes, especially when some of the other factors mentioned below come into play.
- Syllable structure: In some respects phonological processes serve as a means of normalising complex syllabic patterns into more simplex ones, for example some consonant reduction rules simplify the less universal pattern -CC into the preferred -C (see Consonant cluster simplification). The process of /d/-deletion, for example, greatly prefers a schwa in the following syllable, though in some cases short /ɑ/, as in Donderdag, also sometimes conditions for this effect. (See d-deletion).
- Stress placement: Stressed rounded non-back vowels are frequently derounded once stress is moved to another syllable. Note, though, that even in stressed position derounding of such Afrikaans vowels is quite common. (See Vowel derounding).
- Familiarity of lexical items: Unfamiliar words are normally less prone to variation than commonly used ones.
- Usage frequency: unfamiliar words typically have a lower frequency of usage, and are also less prone to variation than commonly used ones, as in 5. (Coetzee and Kawahara 2013).
- Gender of speaker: Female speakers tend to differ from males as to a variety of processes (e.g. Voicing Assimilation, see Progressive voice assimilation, Regressive voice assimilation and /a/ rounding).
- Age of speaker: Due to sound changes, younger speakers frequently differ from older ones e.g. in the case of /a/-rounding (a-rounding).
- Level of education of speaker: Highly educated speakers tend to speak Standard Afrikaans more readily than uneducated ones.
- Geographic origin of speaker: In some regions, typical accents are found; this is in an obvious way reflected in the specific pronunciation of some vowels.
- Ethnicity: Distinct differences are sometimes found in the sound systems of speakers of different races and ethnicities. The nasalization of vowels, for example, is largely absent in Coloured Afrikaans while more readily present among speakers of Standard Afrikaans.
- 2017Kontemporêre Afrikaanse taalkunde.Van Schaik
- 2014Emergent tonogenesis in AfrikaansThe Journal of the Acoustical Society of America1352421
- 1977Nasalering in Afrikaans.Tydskrif vir Geesteswetenskappe1728-46,
- 1990r-Weglating: 'n tipe leksikale veranderlike.Tydskrif vir Geesteswetenskappe3081-99,
- 1990r-Weglating: 'n tipe leksikale veranderlike.Tydskrif vir Geesteswetenskappe3081-99,
- 1991'n Nuwe kyk na [d]-weglating in Afrikaans.Tydskrif vir Geesteswetenskappe31113-127,
- 1992Fonetiek.Academica
- 1987Afrikaanse fonologie.Macmillan
- 1989Die Afrikaanse fonologie: 'n oorsig.Bundels
- 1992Afrikaanse klankleer.Tafelberg
- 1993A grammar of Afrikaans.ReeksMouton de Gruyter
- 2000Voice Assimilation and Segment Reduction in Casual DutchUtrecht: LOTVrije Universiteit te AmsterdamThesis
- 2000Voice Assimilation and Segment Reduction in Casual DutchUtrecht: LOTVrije Universiteit te AmsterdamThesis
- 2000Voice Assimilation and Segment Reduction in Casual DutchUtrecht: LOTVrije Universiteit te AmsterdamThesis
- 1972Sociolinguistic PatternsUniversity of Pennsylvania Press
- 1972Sociolinguistic PatternsUniversity of Pennsylvania Press
- 1927Afrikaanse fonetiek.Juta
- 1996Ontstemming of stemgewing: weer eens oor die v/f-wisseling in Afrikaans.South African Journal of Linguistics = Suid-Afrikaanse Tydskrif vir Taalkunde14109-117,
- 2011Acoustic reduction in conversational Dutch: A quantitative analysis based on automatically generated segmental transcriptionsJournal of Phonetics3996-109
- 1990Multidimensionele beskrywingsmodel vir regressiewe stemassimilasie.South African Journal of Linguistics = Suid-Afrikaanse Tydskrif vir Taalkunde848-58,
- 1990Progressiewe stemassimilasie: 'n 'nuwe' Afrikaanse fonologiese reël?South African Journal of Linguistics = Suid-Afrikaanse Tydskrif vir Taalkunde888-97,
- 1991Regressiewe stemassimilasie in Afrikaans en Nederlands.Literator1297-106,
- 1992Stemassimilasie en segmentsterktehiërargie in Afrikaans.South African Journal of Linguistics = Suid-Afrikaanse Tydskrif vir Taalkunde. Supplement 1310121-134,
- 1994Ontronding in wit en bruin Afrikaans.Literator15121-143,
- 1995Ontronding in twee variëteite van Afrikaans: 'n produksie- en persepsiestudie.Bundels
- 2005Die Afrikaanse diftong /E+/: 'n eksperimentele ondersoek.Southern African Linguistics and Applied Language Studies23319-334,
- 2006Het jou mô en jou pô 'n strôndhuis by Hôrtenbos? Feit of fiksie?Southern African Linguistics and Applied Language Studies2487-100
- 2010Oor die status van die 'oe' in Afrikaans: 'n akoestiese analise.Tydskrif vir Geesteswetenskappe5031-49,
- 2011Ontronding in Afrikaans / Derounding in Afrikaans.Tydskrif vir Geesteswetenskappe511-20,
- 2011Ontronding in Kharkamsafrikaans?
- 2014Die wals van Afrikaanse 'a' met 'l'.Tydskrif vir Geesteswetenskappe54248-266,
- 1992Die fonologie van '-de' en '-te' in Afrikaans.South African Journal of Linguistics = Suid-Afrikaanse Tydskrif vir Taalkunde. Supplement 1310185-204,
- 2006Is spreekstyl en spreektempo sinonieme?: 'n fonologiese ondersoek.Southern African Linguistics and Applied Language Studies24217-233
- 2006Is spreekstyl en spreektempo sinonieme?: 'n fonologiese ondersoek.Southern African Linguistics and Applied Language Studies24217-233
- 1978Oor die fonologie van 'h' en 'j' en 'w' in Afrikaans.Koers4374-95
- 1982Algemene en Afrikaanse generatiewe fonologie.Macmillan
- 1987Die klanksisteem van Vandermerweafrikaans.South African Journal of Linguistics = Suid-Afrikaanse Tydskrif vir Taalkunde584-109,
- 1989Auslautsverskerping: beginsel of reël?: getuienis uit Afrikaans.Tydskrif vir Geesteswetenskappe29105-109,
- 1996Die akoestiese eienskappe van stemlose eksplosiewe van Afrikaans.South African Journal of Linguistics = Suid-Afrikaanse Tydskrif vir Taalkunde. Supplement 341463-82,
- 2017FonologieVan Schaik
- 1978A formal theory of exceptions in generative phonologyDordrechtForis
- 2013Frequency biases in phonological variationNatural Language and Linguistic Theory31(1)47-89
