- Dutch
- Frisian
- Saterfrisian
- Afrikaans
-
- Phonology
- Segment inventory
- Phonotactics
- Phonological processes
- Phonology-morphology interface
- Word stress
- Primary stress in simplex words
- Monomorphemic words
- Diachronic aspects
- Generalizations on stress placement
- Default penultimate stress
- Lexical stress
- The closed penult restriction
- Final closed syllables
- The diphthong restriction
- Superheavy syllables (SHS)
- The three-syllable window
- Segmental restrictions
- Phonetic correlates
- Stress shifts in loanwords
- Quantity-sensitivity
- Secondary stress
- Vowel reduction in unstressed syllables
- Stress in complex words
- Primary stress in simplex words
- Accent & intonation
- Clitics
- Spelling
- Morphology
- Word formation
- Compounding
- Nominal compounds
- Verbal compounds
- Adjectival compounds
- Affixoids
- Coordinative compounds
- Synthetic compounds
- Reduplicative compounds
- Phrase-based compounds
- Elative compounds
- Exocentric compounds
- Linking elements
- Separable complex verbs (SCVs)
- Gapping of complex words
- Particle verbs
- Copulative compounds
- Derivation
- Numerals
- Derivation: inputs and input restrictions
- The meaning of affixes
- Non-native morphology
- Cohering and non-cohering affixes
- Prefixation
- Suffixation
- Nominal suffixation: person nouns
- Conversion
- Pseudo-participles
- Bound forms
- Nouns
- Nominal prefixes
- Nominal suffixes
- -aal and -eel
- -aar
- -aard
- -aat
- -air
- -aris
- -ast
- Diminutives
- -dom
- -een
- -ees
- -el (nominal)
- -elaar
- -enis
- -er (nominal)
- -erd
- -erik
- -es
- -eur
- -euse
- ge...te
- -heid
- -iaan, -aan
- -ief
- -iek
- -ier
- -ier (French)
- -ière
- -iet
- -igheid
- -ij and allomorphs
- -ijn
- -in
- -ing
- -isme
- -ist
- -iteit
- -ling
- -oir
- -oot
- -rice
- -schap
- -schap (de)
- -schap (het)
- -sel
- -st
- -ster
- -t
- -tal
- -te
- -voud
- Verbs
- Adjectives
- Adverbs
- Univerbation
- Neo-classical word formation
- Construction-dependent morphology
- Morphological productivity
- Compounding
- Inflection
- Inflection and derivation
- Allomorphy
- The interface between phonology and morphology
- Word formation
- Syntax
- Preface and acknowledgements
- Verbs and Verb Phrases
- 1 Characterization and classification
- 2 Projection of verb phrases I:Argument structure
- 3 Projection of verb phrases II:Verb frame alternations
- Introduction
- 3.1. Main types
- 3.2. Alternations involving the external argument
- 3.3. Alternations of noun phrases and PPs
- 3.3.1. Dative/PP alternations (dative shift)
- 3.3.1.1. Dative alternation with aan-phrases (recipients)
- 3.3.1.2. Dative alternation with naar-phrases (goals)
- 3.3.1.3. Dative alternation with van-phrases (sources)
- 3.3.1.4. Dative alternation with bij-phrases (possessors)
- 3.3.1.5. Dative alternation with voor-phrases (benefactives)
- 3.3.1.6. Conclusion
- 3.3.1.7. Bibliographical notes
- 3.3.2. Accusative/PP alternations
- 3.3.3. Nominative/PP alternations
- 3.3.1. Dative/PP alternations (dative shift)
- 3.4. Some apparent cases of verb frame alternation
- 3.5. Bibliographical notes
- 4 Projection of verb phrases IIIa:Selection of clauses/verb phrases
- 5 Projection of verb phrases IIIb:Argument and complementive clauses
- Introduction
- 5.1. Finite argument clauses
- 5.2. Infinitival argument clauses
- 5.3. Complementive clauses
- 6 Projection of verb phrases IIIc:Complements of non-main verbs
- 7 Projection of verb phrases IIId:Verb clusters
- 8 Projection of verb phrases IV: Adverbial modification
- 9 Word order in the clause I:General introduction
- 10 Word order in the clause II:Position of the finite verb (verb-first/second)
- 11 Word order in the clause III:Clause-initial position (wh-movement)
- Introduction
- 11.1. The formation of V1- and V2-clauses
- 11.2. Clause-initial position remains (phonetically) empty
- 11.3. Clause-initial position is filled
- 12 Word order in the clause IV:Postverbal field (extraposition)
- 13 Word order in the clause V: Middle field (scrambling)
- 14 Main-clause external elements
- Nouns and Noun Phrases
- 1 Characterization and classification
- 2 Projection of noun phrases I: complementation
- Introduction
- 2.1. General observations
- 2.2. Prepositional and nominal complements
- 2.3. Clausal complements
- 2.4. Bibliographical notes
- 3 Projection of noun phrases II: modification
- Introduction
- 3.1. Restrictive and non-restrictive modifiers
- 3.2. Premodification
- 3.3. Postmodification
- 3.3.1. Adpositional phrases
- 3.3.2. Relative clauses
- 3.3.3. Infinitival clauses
- 3.3.4. A special case: clauses referring to a proposition
- 3.3.5. Adjectival phrases
- 3.3.6. Adverbial postmodification
- 3.4. Bibliographical notes
- 4 Projection of noun phrases III: binominal constructions
- Introduction
- 4.1. Binominal constructions without a preposition
- 4.2. Binominal constructions with a preposition
- 4.3. Bibliographical notes
- 5 Determiners: articles and pronouns
- Introduction
- 5.1. Articles
- 5.2. Pronouns
- 5.3. Bibliographical notes
- 6 Numerals and quantifiers
- 7 Pre-determiners
- Introduction
- 7.1. The universal quantifier al 'all' and its alternants
- 7.2. The pre-determiner heel 'all/whole'
- 7.3. A note on focus particles
- 7.4. Bibliographical notes
- 8 Syntactic uses of noun phrases
- Adjectives and Adjective Phrases
- 1 Characteristics and classification
- 2 Projection of adjective phrases I: Complementation
- 3 Projection of adjective phrases II: Modification
- 4 Projection of adjective phrases III: Comparison
- 5 Attributive use of the adjective phrase
- 6 Predicative use of the adjective phrase
- 7 The partitive genitive construction
- 8 Adverbial use of the adjective phrase
- 9 Participles and infinitives: their adjectival use
- 10 Special constructions
- Adpositions and adpositional phrases
- 1 Characteristics and classification
- Introduction
- 1.1. Characterization of the category adposition
- 1.2. A formal classification of adpositional phrases
- 1.3. A semantic classification of adpositional phrases
- 1.3.1. Spatial adpositions
- 1.3.2. Temporal adpositions
- 1.3.3. Non-spatial/temporal prepositions
- 1.4. Borderline cases
- 1.5. Bibliographical notes
- 2 Projection of adpositional phrases: Complementation
- 3 Projection of adpositional phrases: Modification
- 4 Syntactic uses of the adpositional phrase
- 5 R-pronominalization and R-words
- 1 Characteristics and classification
- Phonology
-
- General
- Phonology
- Segment inventory
- Phonotactics
- Phonological Processes
- Assimilation
- Vowel nasalization
- Syllabic sonorants
- Final devoicing
- Fake geminates
- Vowel hiatus resolution
- Vowel reduction introduction
- Schwa deletion
- Schwa insertion
- /r/-deletion
- d-insertion
- {s/z}-insertion
- t-deletion
- Intrusive stop formation
- Breaking
- Vowel shortening
- h-deletion
- Replacement of the glide w
- Word stress
- Clitics
- Allomorphy
- Orthography of Frisian
- Morphology
- Inflection
- Word formation
- Derivation
- Prefixation
- Infixation
- Suffixation
- Nominal suffixes
- Verbal suffixes
- Adjectival suffixes
- Adverbial suffixes
- Numeral suffixes
- Interjectional suffixes
- Onomastic suffixes
- Conversion
- Compositions
- Derivation
- Syntax
- Verbs and Verb Phrases
- Characteristics and classification
- Unergative and unaccusative subjects
- Evidentiality
- To-infinitival clauses
- Predication and noun incorporation
- Ellipsis
- Imperativus-pro-Infinitivo
- Expression of irrealis
- Embedded Verb Second
- Agreement
- Negation
- Nouns & Noun Phrases
- Classification
- Complementation
- Modification
- Partitive noun constructions
- Referential partitive constructions
- Partitive measure nouns
- Numeral partitive constructions
- Partitive question constructions
- Nominalised quantifiers
- Kind partitives
- Partitive predication with prepositions
- Bare nominal attributions
- Articles and names
- Pronouns
- Quantifiers and (pre)determiners
- Interrogative pronouns
- R-pronouns
- Syntactic uses
- Adjective Phrases
- Characteristics and classification
- Complementation
- Modification and degree quantification
- Comparison by degree
- Comparative
- Superlative
- Equative
- Attribution
- Agreement
- Attributive adjectives vs. prenominal elements
- Complex adjectives
- Noun ellipsis
- Co-occurring adjectives
- Predication
- Partitive adjective constructions
- Adverbial use
- Participles and infinitives
- Adposition Phrases
- Characteristics and classification
- Complementation
- Modification
- Intransitive adpositions
- Predication
- Preposition stranding
- Verbs and Verb Phrases
-
- General
- Morphology
- Morphology
- 1 Word formation
- 1.1 Compounding
- 1.1.1 Compounds and their heads
- 1.1.2 Special types of compounds
- 1.1.2.1 Affixoids
- 1.1.2.2 Coordinative compounds
- 1.1.2.3 Synthetic compounds and complex pseudo-participles
- 1.1.2.4 Reduplicative compounds
- 1.1.2.5 Phrase-based compounds
- 1.1.2.6 Elative compounds
- 1.1.2.7 Exocentric compounds
- 1.1.2.8 Linking elements
- 1.1.2.9 Separable Complex Verbs and Particle Verbs
- 1.1.2.10 Noun Incorporation Verbs
- 1.1.2.11 Gapping
- 1.2 Derivation
- 1.3 Minor patterns of word formation
- 1.1 Compounding
- 2 Inflection
- 1 Word formation
- Morphology
- Syntax
- Adjectives and adjective phrases (APs)
- 0 Introduction to the AP
- 1 Characteristics and classification of APs
- 2 Complementation of APs
- 3 Modification and degree quantification of APs
- 4 Comparison by comparative, superlative and equative
- 5 Attribution of APs
- 6 Predication of APs
- 7 The partitive adjective construction
- 8 Adverbial use of APs
- 9 Participles and infinitives as APs
- Nouns and Noun Phrases (NPs)
- 0 Introduction to the NP
- 1 Characteristics and Classification of NPs
- 2 Complementation of NPs
- 3 Modification of NPs
- 3.1 Modification of NP by Determiners and APs
- 3.2 Modification of NP by PP
- 3.3 Modification of NP by adverbial clauses
- 3.4 Modification of NP by possessors
- 3.5 Modification of NP by relative clauses
- 3.6 Modification of NP in a cleft construction
- 3.7 Free relative clauses and selected interrogative clauses
- 4 Partitive noun constructions and constructions related to them
- 4.1 The referential partitive construction
- 4.2 The partitive construction of abstract quantity
- 4.3 The numerical partitive construction
- 4.4 The partitive interrogative construction
- 4.5 Adjectival, nominal and nominalised partitive quantifiers
- 4.6 Kind partitives
- 4.7 Partitive predication with a preposition
- 4.8 Bare nominal attribution
- 5 Articles and names
- 6 Pronouns
- 7 Quantifiers, determiners and predeterminers
- 8 Interrogative pronouns
- 9 R-pronouns and the indefinite expletive
- 10 Syntactic functions of Noun Phrases
- Adpositions and Adpositional Phrases (PPs)
- 0 Introduction to the PP
- 1 Characteristics and classification of PPs
- 2 Complementation of PPs
- 3 Modification of PPs
- 4 Bare (intransitive) adpositions
- 5 Predication of PPs
- 6 Form and distribution of adpositions with respect to staticity and construction type
- 7 Adpositional complements and adverbials
- Verbs and Verb Phrases (VPs)
- 0 Introduction to the VP in Saterland Frisian
- 1 Characteristics and classification of verbs
- 2 Unergative and unaccusative subjects and the auxiliary of the perfect
- 3 Evidentiality in relation to perception and epistemicity
- 4 Types of to-infinitival constituents
- 5 Predication
- 5.1 The auxiliary of being and its selection restrictions
- 5.2 The auxiliary of going and its selection restrictions
- 5.3 The auxiliary of continuation and its selection restrictions
- 5.4 The auxiliary of coming and its selection restrictions
- 5.5 Modal auxiliaries and their selection restrictions
- 5.6 Auxiliaries of body posture and aspect and their selection restrictions
- 5.7 Transitive verbs of predication
- 5.8 The auxiliary of doing used as a semantically empty finite auxiliary
- 5.9 Supplementive predication
- 6 The verbal paradigm, irregularity and suppletion
- 7 Verb Second and the word order in main and embedded clauses
- 8 Various aspects of clause structure
- Adjectives and adjective phrases (APs)
-
- General
- Phonology
- Afrikaans phonology
- Segment inventory
- Overview of Afrikaans vowels
- The diphthongised long vowels /e/, /ø/ and /o/
- The unrounded mid-front vowel /ɛ/
- The unrounded low-central vowel /ɑ/
- The unrounded low-central vowel /a/
- The rounded mid-high back vowel /ɔ/
- The rounded high back vowel /u/
- The rounded and unrounded high front vowels /i/ and /y/
- The unrounded and rounded central vowels /ə/ and /œ/
- The diphthongs /əi/, /œy/ and /œu/
- Overview of Afrikaans consonants
- The bilabial plosives /p/ and /b/
- The alveolar plosives /t/ and /d/
- The velar plosives /k/ and /g/
- The bilabial nasal /m/
- The alveolar nasal /n/
- The velar nasal /ŋ/
- The trill /r/
- The lateral liquid /l/
- The alveolar fricative /s/
- The velar fricative /x/
- The labiodental fricatives /f/ and /v/
- The approximants /ɦ/, /j/ and /ʋ/
- Overview of Afrikaans vowels
- Word stress
- The phonetic properties of stress
- Primary stress on monomorphemic words in Afrikaans
- Background to primary stress in monomorphemes in Afrikaans
- Overview of the Main Stress Rule of Afrikaans
- The short vowels of Afrikaans
- Long vowels in monomorphemes
- Primary stress on diphthongs in monomorphemes
- Exceptions
- Stress shifts in place names
- Stress shift towards word-final position
- Stress pattern of reduplications
- Phonological processes
- Vowel related processes
- Consonant related processes
- Homorganic glide insertion
- Phonology-morphology interface
- Phonotactics
- Morphology
- Syntax
- Afrikaans syntax
- Nouns and noun phrases
- Characteristics of the NP
- Classification of nouns
- Complementation of NPs
- Modification of NPs
- Binominal and partitive constructions
- Referential partitive constructions
- Partitive measure nouns
- Numeral partitive constructions
- Partitive question constructions
- Partitive constructions with nominalised quantifiers
- Partitive predication with prepositions
- Binominal name constructions
- Binominal genitive constructions
- Bare nominal attribution
- Articles and names
- Pronouns
- Quantifiers, determiners and predeterminers
- Syntactic uses of the noun phrase
- Adjectives and adjective phrases
- Characteristics and classification of the AP
- Complementation of APs
- Modification and Degree Quantification of APs
- Comparison by comparative, superlative and equative degree
- Attribution of APs
- Predication of APs
- The partitive adjective construction
- Adverbial use of APs
- Participles and infinitives as adjectives
- Verbs and verb phrases
- Characterisation and classification
- Argument structure
- Verb frame alternations
- Complements of non-main verbs
- Verb clusters
- Complement clauses
- Adverbial modification
- Word order in the clause: Introduction
- Word order in the clause: position of the finite Verb
- Word order in the clause: Clause-initial position
- Word order in the clause: Extraposition and right-dislocation in the postverbal field
- Word order in the middle field
- Emphatic constructions
- Adpositions and adposition phrases
This section discusses the semantics of spatial adpositions. Subsection I starts by briefly discussing the central semantic notions of (change of) location and direction. Subsection II shows that spatial adpositions can be interpreted in three different ways, which we will refer to as deictic, inherent and absolute, subsections III and IV argue that the mathematical notion of a vector is very useful to properly describe the semantics of spatial adpositions. Subsection V, finally, goes somewhat deeper into the notion of a path that enters the definition of directional PPs.
Spatial adpositions like op'on' in (160) can normally be used in two distinct contexts. Example (160a) is ambiguous between two readings: according to the first reading, Jan is situated on the table and he is jumping there; according to the second reading, Jan is performing the action of jumping as the result of which he ends up in a different location, viz., on the table. The ambiguity of (160) is resolved if the clause is put in the perfect tense: if the auxiliary hebben is used, as in (160b), only the first reading survives; if the auxiliary zijn is used, as in (160c), only the second reading survives.
| a. | Jan springt | op | de tafel. | location or change of location | |
| Jan jumps | on(to) | the table |
| b. | Jan heeft | op | de tafel | gesprongen. | location | |
| Jan has | on | the table | jumped |
| c. | Jan is | op | de tafel | gesprongen. | change of location | |
| Jan has | onto | the table | jumped |
It sometimes claimed that these two different readings are due to the adposition op itself, that is, that we are dealing with two homonymic adpositions which denote, respectively, a location and a change of location. We will not adopt this position, but instead assume that the specific interpretation of the adposition is due to the verb that is used: if springen selects the auxiliary hebben it is used as an atelic verb, and hence no change of location is implied; if springen selects zijn it is used as a telic verb, and hence a change of location is implied. This would be consistent with the fact, illustrated in (161), that most spatial PPs can be used as complements both of locational verbs like liggen'to lie' and staan'to stand' and of verbs of change of location like leggen and zetten'to put'. This shows that adpositions of the sort in (161) are compatible both with a location and with a change of location reading.
| a. | De lamp staat | bij/naast/onder/op | de tafel. | location | |
| the lamp stands | near/next.to/under/on | the table | |||
| 'The lamp is standing near/next to/under/on the table.' | |||||
| a'. | De ladder | ligt | achter/langs/tegen | de muur. | |
| the ladder | lies | behind/along/against | the wall | ||
| 'The ladder is lying behind/along/against the wall.' | |||||
| b. | Jan zet | de lamp | bij/naast/onder/op | de tafel. | change of location | |
| Jan puts | the lamp | near/next.to/under/on | the table | |||
| 'Jan is putting the lamp near/next to/under/on the table.' | ||||||
| b'. | Jan legt | de ladder | achter/langs/tegen | de muur. | |
| Jan puts | the ladder | behind/along/against | the wall | ||
| 'Jan is putting the ladder behind/along/against the wall.' | |||||
A small number of spatial adpositions are exceptional in that they cannot occur as complements of verbs of (change of) location. These adpositions intrinsically denote a path (cf. Subsection V), and since we define the notion of direction as “movement along a path”, we will refer to such adpositions as directional adpositions. Directional PPs typically occur as the complement of verbs of traversing (verbs that denote movement along a certain path), such as rijden'to drive'. In (162) an example is given with the preposition naar'to'.
| Jan | rijdt | naar Groningen. | direction | ||
| Jan | drives | to Groningen | |||
| 'Jan is driving to Groningen.' | |||||
Since the examples in (161) show that the difference between the location and change of location reading of the spatial adpositions is due to the syntactic environment (here: the verb), we may assume that spatial PPs headed by non-directional spatial adpositions simply refer to some point or region in space. We will therefore simply use the term locational adposition for such non-directional spatial adpositions.
The basic meaning contribution of the locational adpositions is that they establish a spatial relation between two entities. The locational prepositional phrase in het huis'in the house' in (163), for example, situates the subject of the clause Jan in space, which we may therefore call the located object (other terms found in the literature on spatial relations are theme, figure and trajectory). More precisely, the located object is situated in space with respect to the complement of the preposition het huis'the house', which we may therefore call the reference object (other terms found in the literature are ground and landmark). The precise nature of the spatial relation is determined by the lexical meaning of the locational preposition in'in'; the relation would have been different if we had used voor'in front of' instead of in. Therefore, as a first approximation, it seems reasonable to consider the preposition in as a two-place predicate, and assign the clause in (163a) the meaning in (163b).
| a. | Jan is in het huis. | |
| Jan is in the house |
| b. | in (Jan, het huis) |
The meaning assignment to the clause in (163a) seems rather straightforward: Jan is situated inside the house. In some cases, however, things are not that simple. There are actually three different ways in which locational prepositions can be interpreted.
Consider example (164a). Assigning this example the semantic representation in (164b) seems to somehow miss the point; see the discussion in Subsection B for an account of this. This representation only establishes a relation between the located and the reference object, whereas a third participant seems to be involved: a speaker who utters (164a) seems to compute the position of Jan in relation to both the tree and himself. Example (164a) refers to the situation in Figure 1B; the situation in Figure 1A seems somehow undefined.
| a. | Jan staat | voor | de boom. | |
| Jan stands | in.front.of | the tree |
| b. | voor (Jan, de boom) |
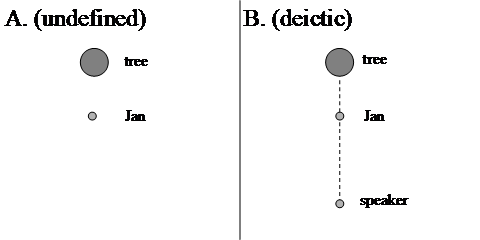
The interpretation in Figure 1B, which is dependent on some additional anchoring point that also enters into the computation of the location of the located object, is called deictic. When an adpositional phrase is interpreted deictically, we will indicate this in the semantic representation by means of a D in superscript after the adposition: PD (x,y). That we are dealing with the anchoring point z can be indicated as follows: PD,z (x,y). Example (164a), that is, the situation depicted in Figure 1B, can therefore be represented as in (165), in which D,s indicates that we are dealing with a deictic interpretation of the preposition voor with the speaker s as its anchoring point.
| voorD,s (Jan, de boom) |
The examples in (166) show that the anchoring point need not be the speaker. In (166a) the anchoring point is the addressee a, and in (166b) it is some other participant in the discourse, viz., de kerk'the church'.
| a. | Vanuit | jou | gezien, | staat | Jan recht | voor de boom. | |
| from | you | seen | stands | Jan straight | in.front.of the tree | ||
| 'Seen from your position, Jan is standing right in front of the tree.' | |||||||
| a'. | voorD,a (Jan, de boom) |
| b. | Vanuit | de kerk | gezien, | staat | Jan recht | voor de boom. | |
| from | the church | seen | stands | Jan straight | in.front.of the tree | ||
| 'Seen from the church, Jan is standing right in front of the tree.' | |||||||
| b'. | voorD,de kerk (Jan, de boom) |
The anchoring point from which the location of the located object is computed may also be the reference object, that is, the complement of the adposition. This is only possible if the reference object is structured with respect to the relevant dimension(s). Consider example (167a), which can be depicted as in Figure 2A, in which the location of Jan is computed by taking the reference object as the anchoring point; the position of the speaker with respect to Jan and the car is not relevant. The difference between (164a) and (167a) has to do with the dimensional structuring of the reference object; a car can be seen as an object with a back and a front (indicated in Figure 2A by means of an arrow through the object), whereas we normally do not perceive trees in that way. Because of these dimensional properties of cars and trees, we can take the first but not the latter as the anchoring point for the preposition voor. The interpretation of locational adpositions in which we take the reference object as the anchoring point will be called inherent and from now on be indicated by means of an I in superscript: PI. On the inherent interpretation, example (167a) can therefore be represented as in (167b). Observe that the deictic interpretation is possible as well; (167a) can also refer to the situation depicted in Figure 2B, which can be assigned the semantic representation in (167c).
| a. | Jan staat | voor | de auto. | |
| Jan stands | in.front.of | the car | ||
| 'Jan is standing in front of the car.' | ||||
| b. | voorI (Jan, de auto) |
| c. | voorD,s (Jan, de auto) |
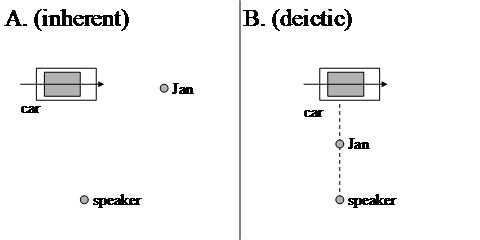
The deictic and the inherent interpretations of adpositional phrases differ in their logical properties. This can be illustrated by means of the examples in (168). When we interpret the adpositions deictically, the conclusion in (168c) follows from (168a&b), as can be seen in Figure 3A. However, if we interpret the adpositions inherently, the inference in (168) is no longer valid, as is shown in Figure 3B. The same difference in logical properties holds for other adpositions that can be used both deictically and inherently, like the simple prepositions achter'behind', naast'next to' and the phrasal prepositions links/rechts van'to the left/right of'.
| a. | De auto staat voor de kerk. | AND | |
| 'The car is standing in front of the church.' | |||
| b. | Jan staat voor de auto. | ⇒ | |
| 'Jan is standing in front of the car.' | |||
| c. | Jan staat voor de kerk. | |
| 'Jan is standing in front of the church.' |
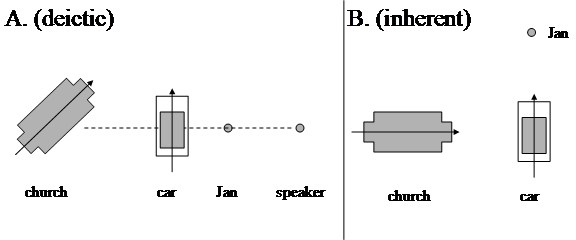
The inference in (168) is also invalid if we switch from one perspective to another. The preposition in in (169a) is inherent, whereas the preposition voor in (169b) is interpreted deictically; cf. Figure 1. From these two examples, we cannot conclude that (169c) holds: for example, if Jan is situated in front of the trunk of the tree, and the bird is in the top of the tree, (169c) will clearly be false.
| a. | De vogel | is | in de boom. AND | |
| the bird | is | in the tree |
| b. | Jan staat | voor | de boom. ⇏ | |
| Jan stands | in.front.of | the tree |
| c. | Jan staat | voor | de vogel. | |
| Jan stands | in.front.of | the bird |
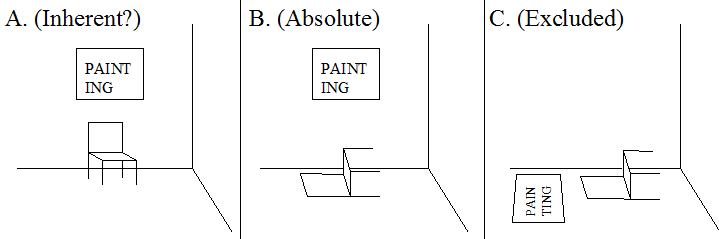
Consider example (170a), which can be depicted as in Figure 4A. The fact that the computation of the location of the painting is independent of the speaker suggests that we are dealing with an inherent interpretation of the prepositional phrase boven die stoel 'above that chair' : bovenI (het schilderij, de stoel). This would be consistent with the fact that a chair can be considered to have a bottom and a top. There is reason to doubt, however, that the dimensions of the chair are really involved in the computation, because (170a) can also be felicitously used to refer to the situation depicted in Figure 4B, where the constellation between the chair and the painting has been changed. Moreover, (170a) cannot be used to refer to the situation in Figure 4C, where the constellation between the chair and the painting is essentially the same as in Figure 4C; note, for completeness' sake that (170a) is also unable to refer to the situation in Figure 4C when we replace the verb hangen by liggen 'to lie' , which may provide a more appropriate description of the positioning of the painting. Interpretations of adpositional phrases that have neither an internal nor an external anchoring point will be called absolute (that is, depending only on the natural environment such as the surface of the earth); these interpretations will be indicated without a superscript, as in (170b).
| a. | Het schilderij | hangt | boven | die stoel. | |
| the painting | hangs | above | that chair | ||
| 'The painting is hanging above that chair.' | |||||
| b. | boven (het schilderij, de stoel) |
Locational adpositions locate an object in space with respect to the reference object. It should be noted, however, that the interpretation of locational PPs is often rather vague. Consider the examples in (171). Example (171a) is most naturally interpreted in such a way that the photographer is standing in the position depicted in Figure 5. Example (171b), on the other hand, need not be interpreted in such a way that all the lamps are positioned like lamp 3; they may also occupy the positions of the other lamps as long as they remain in the grey area.
| a. | De fotograaf | staat | achter de camera. | |
| the photographer | stands | behind the camera | ||
| 'The photographer is standing behind the camera.' | ||||
| b. | De lampen | staan | achter de camera. | |
| the lamps | stand | behind the camera | ||
| 'The lamps are behind the camera.' | ||||
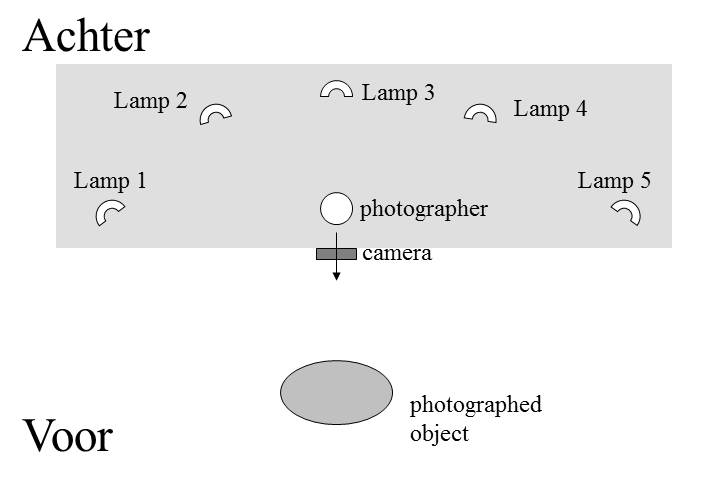
Figure 5 shows that locational PPs sometimes refer to rather extensive regions. As a result of this the regions denoted by different locational adpositions may overlap. For example, if we specifically want to refer to lamp 1 in Figure 5, we could also say that it stands naast'next to' or links van'to the left of' the camera. We can even express the appropriateness of the chosen adpositions by means of examples such as (172), which makes explicit that achter'behind' and naast “next to' are both applicable, but that naast is the most appropriate preposition to express the intended spatial relation.
| Lamp 1 | staat | meer naast | dan | achter de camera. | ||
| lamp 1 | stands | more next.to | than | behind the camera | ||
| 'Lamp 1 is situated more next to than behind the camera.' | ||||||
The positions in the region can also be made more specific by modifying the prepositional phrase. If we interpret the preposition achter deictically from the point of view of the object photographed, the statements in (173) are true. Note in passing that according to the inherent interpretation of achter, which takes the camera as its anchoring point, lamp 2 would be to the right of the camera.
| a. | Lamp 3 | staat | recht | achter de camera. | |
| lamp 3 | stands | straight | behind the camera | ||
| 'Lamp 3 is positioned straight behind the camera.' | |||||
| b. | Lamp 2 | staat | links | achter de camera. | |
| lamp 2 | stands | left | behind the camera | ||
| 'Lamp 2 is positioned to the left behind the camera.' | |||||
The examples in (173) give an indication of the direction we have to look in order to find the located object in question. As is shown in (174), the distance between the reference and the located object can also be indicated.
| a. | De fotograaf | staat | vlak | achter de camera. | |
| the photographer | stands | right | behind the camera | ||
| 'The photographer is standing right behind the camera.' | |||||
| b. | Lamp 3 | staat | vijf meter | achter de camera. | |
| lamp 3 | stands | five meters | behind the camera | ||
| 'Lamp 3 is positioned five meters behind the camera.' | |||||
This means that each point in the region referred to by the locational PP achter de camera can be defined by means of a direction and a distance. In other words, the preposition achter can be considered to denote a set of vectors that project the position of the reference object onto a potential position of the located object. Consider Figure 6 in which the reference object occupies the (0,0) position. The preposition achter denotes those vectors V‹x,y› that originate in (0,0), and for which y > 0; since the vectors V‹-4,3›, V‹0,5› and V‹8,1› map the position of the reference object onto the positions of lamps 2, 3 and 5, respectively, the latter are indeed in the region referred to by the PP achter de camera.
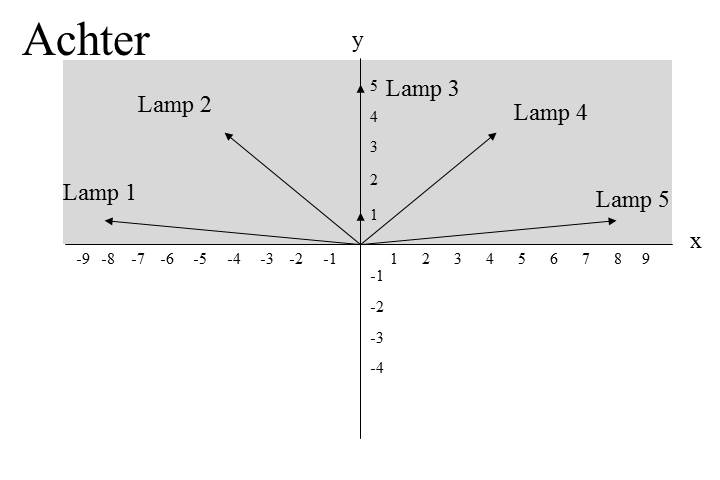
We can also denote subsets of the set of vectors denoted by the PP achter de camera 'behind the camera' : the modified PP recht achter de camera 'straight behind the camera' denotes the subset of vectors denoted by achter in which x = 0, the modified PP links achter de camera denotes the subset of vectors in which x < 0, and the modified PP rechts achter de camera denotes the subset of vectors in which x > 0. Furthermore, the modified PP vlak achter de camera denotes the subset of vectors that are smaller than some contextually determined magnitude (length). These examples show that the assumption that locational prepositions denote a set of vectors will be very useful in the discussion of the modification properties of locational PPs in Section 3.1. For the moment, however, it suffices to observe that locational PPs refer to regions instead of fixed points in space.
Prepositions like achter'behind', and boven'above' seem to express that the magnitude of the vector is larger than zero, that is, that there is some distance between the reference object and the located object. Other prepositions, however, require there to be some physical contact between the two objects: they require that the magnitude of the vector be zero. This difference can be illustrated by means of the prepositions op'on' and boven'above' in (175); example (175a) implies that there is physical contact between the table and the lamp, as in Figure 7A, whereas (175b) suggests the absence of such contact, as in Figure 7B.
| a. | De lamp | staat | op de tafel. | |
| the lamp | stands | on the table | ||
| 'The lamp is standing on the table.' | ||||
| b. | De lamp | hangt | boven de tafel. | |
| the lamp | hangs | above the table | ||
| 'The lamp is hanging above the table.' | ||||
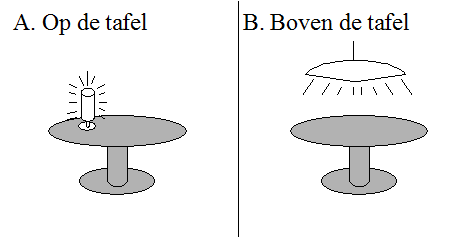
Note that the choice of verb does not affect the interpretation of the preposition; substituting hangen for staan in (175b) is possible if we refer to a situation like Figure 7B, in which the lamp is hanging so low that it touches the table. Somewhat more common examples such as this are given in (176).
| a. | De gordijnen | hangen | op de vensterbank. | |
| the curtains | hung | on the windowsill | ||
| 'The curtains are touching the windowsill.' | ||||
| b. | Je rok | hangt | op de grond. | |
| your skirt | hangs | on the floor | ||
| 'The hem of your skirt is touching the floor.' | ||||
The fact that the preposition op denotes the null vector, whereas boven denotes a larger set of vectors with a magnitude greater than 0 accounts for the fact that (on the idealization that the length of the part of the square adjacent to the church does not exceed the length of the side of the church adjacent to the square) the inference in (177) is valid, whereas the one in (178) is not.
| a. | Jan loopt op het plein. | AND | |
| 'Jan is walking on the square.' | |||
| b. | Het plein is voor de kerk. | ⇒ | |
| 'The square is in front of the church.' | |||
| c. | Jan loopt voor de kerk. | |
| 'Jan is walking in front of the church.' |
| a. | De luchtballon zweeft boven het plein. | AND | |
| 'The hot-air balloon is floating above the square.' | |||
| b. | Het plein is voor de kerk. | ⇏ | |
| 'The square is in front of the church.' | |||
| c. | De luchtballon zweeft voor de kerk. | |
| 'The hot-air balloon is floating in front of the church.' |
There is, however, also a potential problem for the claim that the denotations of prepositions like achter and boven do not include the null vector. If we assume that the meaning of achter/boven op in (179) is compositionally determined, we should conclude that achter and boven are compatible with the null vector since otherwise a contradiction would arise.
| a. | De productiedatum | staat | achter | op | het blik. | |
| the manufacturing.date | stands | behind | on | the can | ||
| 'The manufacturing date can be found on the back of the can.' | ||||||
| b. | De productiedatum | staat | boven | op | het blik. | |
| the manufacturing.date | stands | above | on | the can | ||
| 'The manufacturing date can be found on top of the can.' | ||||||
We will not discuss this problem here, but simply claim that the underlying assumption that the meanings of achter/boven op is compositionally determined is false. Section 3.1.3 will show that formations like achterop and bovenop are compounds, and we therefore expect that the denotation of these formations consists of a subset of the denotation of the second member, the preposition op. Given that the reference object het blik in (179) is not a point in space but a three-dimensional object, the preposition op can be assumed to denote a non-singleton set of null vectors which are situated at different positions on the surface of the reference object, and it is therefore correctly predicted that the compounds achterop and bovenop denote distinct subsets of this set of null vectors denoted by op.
Although the discussion of the examples in (179) clearly shows that this is, strictly speaking, not correct, we will often take the reference object to be a point in space instead of a physical object with three-dimensional extensions in order to simplify the discussion that will follow; this motivates why we will normally refer to “the null vector” instead of “the set of null vectors”. The three-dimensional extensions of the reference object will only be taken into account if this is necessary for the discussion.
Directional adpositions differ from locational ones in that they do not situate the located object in a fixed position in space. As a result, the denotation of a di rectional preposition cannot simply be considered a set of vectors. This does not imply, however, that the notion of vector is irrelevant in the case of directional PPs. Directional PPs express that the located object traverses a certain path. A path can be defined as an ordered set of vectors, each of which is associated with a certain position on the time line. The path denoted by van A naar B'from A to B' can then be represented as in Figure 8, which can be read as a cartoon. In our visual representations below, we will often indicate paths by means of a blocked or dotted arrow.
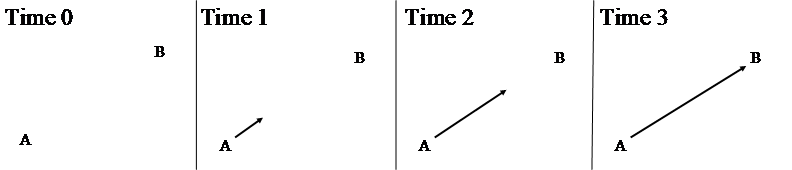
The situation depicted in Figure 8 is an appropriate characterization of the directional phrase in (a), in which the PPs act as complements of the verb of traversing rijden'to drive'. Besides this “core” directional reading, directional PPs can also have two slightly different readings. The PPs in (180b) do not denote a path that is traversed, but indicate the extent of the located object deze weg'the road'; this example expresses that the road is situated on a path that goes from Utrecht to Groningen. We will refer to this use of the PP in (180b) as the extent reading (note that the verb lopen is also used as a verb of traversing meaning “to walk” if the subject is animate). The directional PP in (180c), finally, is used with an orientation reading.
| a. | Jan rijdt | van Utrecht | naar Groningen. | directional reading | |
| Jan drives | from Utrecht | to Groningen |
| b. | Deze weg | loopt | van Utrecht | naar Groningen. | extent reading | |
| this road | goes | from Utrecht | to Groningen |
| c. | De richtingaanwijzer | wijst | naar Groningen. | orientation reading | |
| the direction.sign | points | to Groningen |
