- Dutch
- Frisian
- Saterfrisian
- Afrikaans
-
- Phonology
- Segment inventory
- Phonotactics
- Phonological processes
- Phonology-morphology interface
- Word stress
- Primary stress in simplex words
- Monomorphemic words
- Diachronic aspects
- Generalizations on stress placement
- Default penultimate stress
- Lexical stress
- The closed penult restriction
- Final closed syllables
- The diphthong restriction
- Superheavy syllables (SHS)
- The three-syllable window
- Segmental restrictions
- Phonetic correlates
- Stress shifts in loanwords
- Quantity-sensitivity
- Secondary stress
- Vowel reduction in unstressed syllables
- Stress in complex words
- Primary stress in simplex words
- Accent & intonation
- Clitics
- Spelling
- Morphology
- Word formation
- Compounding
- Nominal compounds
- Verbal compounds
- Adjectival compounds
- Affixoids
- Coordinative compounds
- Synthetic compounds
- Reduplicative compounds
- Phrase-based compounds
- Elative compounds
- Exocentric compounds
- Linking elements
- Separable complex verbs (SCVs)
- Gapping of complex words
- Particle verbs
- Copulative compounds
- Derivation
- Numerals
- Derivation: inputs and input restrictions
- The meaning of affixes
- Non-native morphology
- Cohering and non-cohering affixes
- Prefixation
- Suffixation
- Nominal suffixation: person nouns
- Conversion
- Pseudo-participles
- Bound forms
- Nouns
- Nominal prefixes
- Nominal suffixes
- -aal and -eel
- -aar
- -aard
- -aat
- -air
- -aris
- -ast
- Diminutives
- -dom
- -een
- -ees
- -el (nominal)
- -elaar
- -enis
- -er (nominal)
- -erd
- -erik
- -es
- -eur
- -euse
- ge...te
- -heid
- -iaan, -aan
- -ief
- -iek
- -ier
- -ier (French)
- -ière
- -iet
- -igheid
- -ij and allomorphs
- -ijn
- -in
- -ing
- -isme
- -ist
- -iteit
- -ling
- -oir
- -oot
- -rice
- -schap
- -schap (de)
- -schap (het)
- -sel
- -st
- -ster
- -t
- -tal
- -te
- -voud
- Verbs
- Adjectives
- Adverbs
- Univerbation
- Neo-classical word formation
- Construction-dependent morphology
- Morphological productivity
- Compounding
- Inflection
- Inflection and derivation
- Allomorphy
- The interface between phonology and morphology
- Word formation
- Syntax
- Preface and acknowledgements
- Verbs and Verb Phrases
- 1 Characterization and classification
- 2 Projection of verb phrases I:Argument structure
- 3 Projection of verb phrases II:Verb frame alternations
- Introduction
- 3.1. Main types
- 3.2. Alternations involving the external argument
- 3.3. Alternations of noun phrases and PPs
- 3.3.1. Dative/PP alternations (dative shift)
- 3.3.1.1. Dative alternation with aan-phrases (recipients)
- 3.3.1.2. Dative alternation with naar-phrases (goals)
- 3.3.1.3. Dative alternation with van-phrases (sources)
- 3.3.1.4. Dative alternation with bij-phrases (possessors)
- 3.3.1.5. Dative alternation with voor-phrases (benefactives)
- 3.3.1.6. Conclusion
- 3.3.1.7. Bibliographical notes
- 3.3.2. Accusative/PP alternations
- 3.3.3. Nominative/PP alternations
- 3.3.1. Dative/PP alternations (dative shift)
- 3.4. Some apparent cases of verb frame alternation
- 3.5. Bibliographical notes
- 4 Projection of verb phrases IIIa:Selection of clauses/verb phrases
- 5 Projection of verb phrases IIIb:Argument and complementive clauses
- Introduction
- 5.1. Finite argument clauses
- 5.2. Infinitival argument clauses
- 5.3. Complementive clauses
- 6 Projection of verb phrases IIIc:Complements of non-main verbs
- 7 Projection of verb phrases IIId:Verb clusters
- 8 Projection of verb phrases IV: Adverbial modification
- 9 Word order in the clause I:General introduction
- 10 Word order in the clause II:Position of the finite verb (verb-first/second)
- 11 Word order in the clause III:Clause-initial position (wh-movement)
- Introduction
- 11.1. The formation of V1- and V2-clauses
- 11.2. Clause-initial position remains (phonetically) empty
- 11.3. Clause-initial position is filled
- 12 Word order in the clause IV:Postverbal field (extraposition)
- 13 Word order in the clause V: Middle field (scrambling)
- 14 Main-clause external elements
- Nouns and Noun Phrases
- 1 Characterization and classification
- 2 Projection of noun phrases I: complementation
- Introduction
- 2.1. General observations
- 2.2. Prepositional and nominal complements
- 2.3. Clausal complements
- 2.4. Bibliographical notes
- 3 Projection of noun phrases II: modification
- Introduction
- 3.1. Restrictive and non-restrictive modifiers
- 3.2. Premodification
- 3.3. Postmodification
- 3.3.1. Adpositional phrases
- 3.3.2. Relative clauses
- 3.3.3. Infinitival clauses
- 3.3.4. A special case: clauses referring to a proposition
- 3.3.5. Adjectival phrases
- 3.3.6. Adverbial postmodification
- 3.4. Bibliographical notes
- 4 Projection of noun phrases III: binominal constructions
- Introduction
- 4.1. Binominal constructions without a preposition
- 4.2. Binominal constructions with a preposition
- 4.3. Bibliographical notes
- 5 Determiners: articles and pronouns
- Introduction
- 5.1. Articles
- 5.2. Pronouns
- 5.3. Bibliographical notes
- 6 Numerals and quantifiers
- 7 Pre-determiners
- Introduction
- 7.1. The universal quantifier al 'all' and its alternants
- 7.2. The pre-determiner heel 'all/whole'
- 7.3. A note on focus particles
- 7.4. Bibliographical notes
- 8 Syntactic uses of noun phrases
- Adjectives and Adjective Phrases
- 1 Characteristics and classification
- 2 Projection of adjective phrases I: Complementation
- 3 Projection of adjective phrases II: Modification
- 4 Projection of adjective phrases III: Comparison
- 5 Attributive use of the adjective phrase
- 6 Predicative use of the adjective phrase
- 7 The partitive genitive construction
- 8 Adverbial use of the adjective phrase
- 9 Participles and infinitives: their adjectival use
- 10 Special constructions
- Adpositions and adpositional phrases
- 1 Characteristics and classification
- Introduction
- 1.1. Characterization of the category adposition
- 1.2. A formal classification of adpositional phrases
- 1.3. A semantic classification of adpositional phrases
- 1.3.1. Spatial adpositions
- 1.3.2. Temporal adpositions
- 1.3.3. Non-spatial/temporal prepositions
- 1.4. Borderline cases
- 1.5. Bibliographical notes
- 2 Projection of adpositional phrases: Complementation
- 3 Projection of adpositional phrases: Modification
- 4 Syntactic uses of the adpositional phrase
- 5 R-pronominalization and R-words
- 1 Characteristics and classification
- Phonology
-
- General
- Phonology
- Segment inventory
- Phonotactics
- Phonological Processes
- Assimilation
- Vowel nasalization
- Syllabic sonorants
- Final devoicing
- Fake geminates
- Vowel hiatus resolution
- Vowel reduction introduction
- Schwa deletion
- Schwa insertion
- /r/-deletion
- d-insertion
- {s/z}-insertion
- t-deletion
- Intrusive stop formation
- Breaking
- Vowel shortening
- h-deletion
- Replacement of the glide w
- Word stress
- Clitics
- Allomorphy
- Orthography of Frisian
- Morphology
- Inflection
- Word formation
- Derivation
- Prefixation
- Infixation
- Suffixation
- Nominal suffixes
- Verbal suffixes
- Adjectival suffixes
- Adverbial suffixes
- Numeral suffixes
- Interjectional suffixes
- Onomastic suffixes
- Conversion
- Compositions
- Derivation
- Syntax
- Verbs and Verb Phrases
- Characteristics and classification
- Unergative and unaccusative subjects
- Evidentiality
- To-infinitival clauses
- Predication and noun incorporation
- Ellipsis
- Imperativus-pro-Infinitivo
- Expression of irrealis
- Embedded Verb Second
- Agreement
- Negation
- Nouns & Noun Phrases
- Classification
- Complementation
- Modification
- Partitive noun constructions
- Referential partitive constructions
- Partitive measure nouns
- Numeral partitive constructions
- Partitive question constructions
- Nominalised quantifiers
- Kind partitives
- Partitive predication with prepositions
- Bare nominal attributions
- Articles and names
- Pronouns
- Quantifiers and (pre)determiners
- Interrogative pronouns
- R-pronouns
- Syntactic uses
- Adjective Phrases
- Characteristics and classification
- Complementation
- Modification and degree quantification
- Comparison by degree
- Comparative
- Superlative
- Equative
- Attribution
- Agreement
- Attributive adjectives vs. prenominal elements
- Complex adjectives
- Noun ellipsis
- Co-occurring adjectives
- Predication
- Partitive adjective constructions
- Adverbial use
- Participles and infinitives
- Adposition Phrases
- Characteristics and classification
- Complementation
- Modification
- Intransitive adpositions
- Predication
- Preposition stranding
- Verbs and Verb Phrases
-
- General
- Morphology
- Morphology
- 1 Word formation
- 1.1 Compounding
- 1.1.1 Compounds and their heads
- 1.1.2 Special types of compounds
- 1.1.2.1 Affixoids
- 1.1.2.2 Coordinative compounds
- 1.1.2.3 Synthetic compounds and complex pseudo-participles
- 1.1.2.4 Reduplicative compounds
- 1.1.2.5 Phrase-based compounds
- 1.1.2.6 Elative compounds
- 1.1.2.7 Exocentric compounds
- 1.1.2.8 Linking elements
- 1.1.2.9 Separable Complex Verbs and Particle Verbs
- 1.1.2.10 Noun Incorporation Verbs
- 1.1.2.11 Gapping
- 1.2 Derivation
- 1.3 Minor patterns of word formation
- 1.1 Compounding
- 2 Inflection
- 1 Word formation
- Morphology
- Syntax
- Adjectives and adjective phrases (APs)
- 0 Introduction to the AP
- 1 Characteristics and classification of APs
- 2 Complementation of APs
- 3 Modification and degree quantification of APs
- 4 Comparison by comparative, superlative and equative
- 5 Attribution of APs
- 6 Predication of APs
- 7 The partitive adjective construction
- 8 Adverbial use of APs
- 9 Participles and infinitives as APs
- Nouns and Noun Phrases (NPs)
- 0 Introduction to the NP
- 1 Characteristics and Classification of NPs
- 2 Complementation of NPs
- 3 Modification of NPs
- 3.1 Modification of NP by Determiners and APs
- 3.2 Modification of NP by PP
- 3.3 Modification of NP by adverbial clauses
- 3.4 Modification of NP by possessors
- 3.5 Modification of NP by relative clauses
- 3.6 Modification of NP in a cleft construction
- 3.7 Free relative clauses and selected interrogative clauses
- 4 Partitive noun constructions and constructions related to them
- 4.1 The referential partitive construction
- 4.2 The partitive construction of abstract quantity
- 4.3 The numerical partitive construction
- 4.4 The partitive interrogative construction
- 4.5 Adjectival, nominal and nominalised partitive quantifiers
- 4.6 Kind partitives
- 4.7 Partitive predication with a preposition
- 4.8 Bare nominal attribution
- 5 Articles and names
- 6 Pronouns
- 7 Quantifiers, determiners and predeterminers
- 8 Interrogative pronouns
- 9 R-pronouns and the indefinite expletive
- 10 Syntactic functions of Noun Phrases
- Adpositions and Adpositional Phrases (PPs)
- 0 Introduction to the PP
- 1 Characteristics and classification of PPs
- 2 Complementation of PPs
- 3 Modification of PPs
- 4 Bare (intransitive) adpositions
- 5 Predication of PPs
- 6 Form and distribution of adpositions with respect to staticity and construction type
- 7 Adpositional complements and adverbials
- Verbs and Verb Phrases (VPs)
- 0 Introduction to the VP in Saterland Frisian
- 1 Characteristics and classification of verbs
- 2 Unergative and unaccusative subjects and the auxiliary of the perfect
- 3 Evidentiality in relation to perception and epistemicity
- 4 Types of to-infinitival constituents
- 5 Predication
- 5.1 The auxiliary of being and its selection restrictions
- 5.2 The auxiliary of going and its selection restrictions
- 5.3 The auxiliary of continuation and its selection restrictions
- 5.4 The auxiliary of coming and its selection restrictions
- 5.5 Modal auxiliaries and their selection restrictions
- 5.6 Auxiliaries of body posture and aspect and their selection restrictions
- 5.7 Transitive verbs of predication
- 5.8 The auxiliary of doing used as a semantically empty finite auxiliary
- 5.9 Supplementive predication
- 6 The verbal paradigm, irregularity and suppletion
- 7 Verb Second and the word order in main and embedded clauses
- 8 Various aspects of clause structure
- Adjectives and adjective phrases (APs)
-
- General
- Phonology
- Afrikaans phonology
- Segment inventory
- Overview of Afrikaans vowels
- The diphthongised long vowels /e/, /ø/ and /o/
- The unrounded mid-front vowel /ɛ/
- The unrounded low-central vowel /ɑ/
- The unrounded low-central vowel /a/
- The rounded mid-high back vowel /ɔ/
- The rounded high back vowel /u/
- The rounded and unrounded high front vowels /i/ and /y/
- The unrounded and rounded central vowels /ə/ and /œ/
- The diphthongs /əi/, /œy/ and /œu/
- Overview of Afrikaans consonants
- The bilabial plosives /p/ and /b/
- The alveolar plosives /t/ and /d/
- The velar plosives /k/ and /g/
- The bilabial nasal /m/
- The alveolar nasal /n/
- The velar nasal /ŋ/
- The trill /r/
- The lateral liquid /l/
- The alveolar fricative /s/
- The velar fricative /x/
- The labiodental fricatives /f/ and /v/
- The approximants /ɦ/, /j/ and /ʋ/
- Overview of Afrikaans vowels
- Word stress
- The phonetic properties of stress
- Primary stress on monomorphemic words in Afrikaans
- Background to primary stress in monomorphemes in Afrikaans
- Overview of the Main Stress Rule of Afrikaans
- The short vowels of Afrikaans
- Long vowels in monomorphemes
- Primary stress on diphthongs in monomorphemes
- Exceptions
- Stress shifts in place names
- Stress shift towards word-final position
- Stress pattern of reduplications
- Phonological processes
- Vowel related processes
- Consonant related processes
- Homorganic glide insertion
- Phonology-morphology interface
- Phonotactics
- Morphology
- Syntax
- Afrikaans syntax
- Nouns and noun phrases
- Characteristics of the NP
- Classification of nouns
- Complementation of NPs
- Modification of NPs
- Binominal and partitive constructions
- Referential partitive constructions
- Partitive measure nouns
- Numeral partitive constructions
- Partitive question constructions
- Partitive constructions with nominalised quantifiers
- Partitive predication with prepositions
- Binominal name constructions
- Binominal genitive constructions
- Bare nominal attribution
- Articles and names
- Pronouns
- Quantifiers, determiners and predeterminers
- Syntactic uses of the noun phrase
- Adjectives and adjective phrases
- Characteristics and classification of the AP
- Complementation of APs
- Modification and Degree Quantification of APs
- Comparison by comparative, superlative and equative degree
- Attribution of APs
- Predication of APs
- The partitive adjective construction
- Adverbial use of APs
- Participles and infinitives as adjectives
- Verbs and verb phrases
- Characterisation and classification
- Argument structure
- Verb frame alternations
- Complements of non-main verbs
- Verb clusters
- Complement clauses
- Adverbial modification
- Word order in the clause: Introduction
- Word order in the clause: position of the finite Verb
- Word order in the clause: Clause-initial position
- Word order in the clause: Extraposition and right-dislocation in the postverbal field
- Word order in the middle field
- Emphatic constructions
- Adpositions and adposition phrases
From a semantic point of view, set-denoting adjectives denote properties and in this respect they differ from verbs and nouns, which normally denote events and entities, respectively. From the perspective of set theory, on the other hand, verbs, nouns and adjectives are similar in the sense that they all denote sets of entities. An intransitive verb such as wandelen 'to walk' denotes all entities in the domain of discourse that are walking, e.g., “Jan", “Peter" and “Marie". A noun such as jongen 'boy' denotes all entities that have the property of being a boy, e.g., “Jan", “Peter" and “Henk". And, finally, an adjective such as groot 'big' denotes all entities that have the property of being big, e.g., “Jan", “Henk" and “het gebouw" (the building). The domain of discourse that has been set up can be represented as in (36); the entities that are mentioned between the curly brackets are part of the sets that are denoted by the relevant word.
| a. | wandelenV: {Jan, Peter, Marie} |
| b. | jongenN: {Jan, Peter, Henk} |
| c. | grootA: {Jan, Henk, het gebouw} |
Given that some entities are placed within more than one set, a more proper representation of our domain of discourse can be given as in Figure 1, where the relevant entities are placed in the intersections of the three sets.
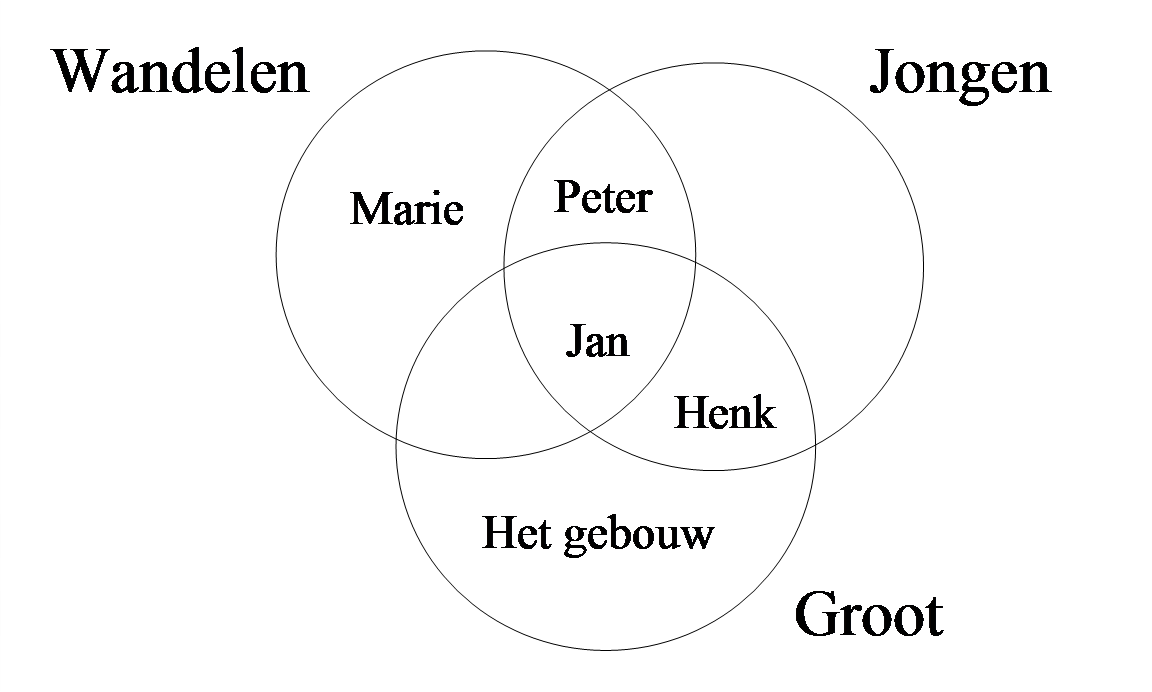
Note that we have simplified the discussion above by ignoring the fact that, e.g., transitive verbs or adjectives that take a PP-complement do not denote entities but ordered pairs of entities: a verb like slaan 'to hit' denotes all ordered pairs <x,y> such that x hits y; similarly, an adjective like trots 'proud' denotes all ordered pairs <x,y> such that x is proud of y. Some verbs and adjectives may even denote ordered triples or quadruples of entities. We will not discuss this any further here since this will lead us into a discussion of complementation, which is the topic of Chapter 2. This section will continue with a brief discussion of the syntactic uses of the set-denoting adjectives: Subsection I will begin with their attributive and predicative uses, which are the most common ones, followed by their adverbial use in Section II.
This subsection briefly discusses the attributive and predicative uses of adjectives, subsection A will start by discussing the interpretation that is typically associated with these uses: an attributive adjective normally enters into an intersection relation with the modified noun, giving rise to a so-called restrictive interpretation, whereas a predicative construction instead enters into an inclusion relation with the noun phrase it is predicated of, subsection B will show, however, that there are also cases in which attributive adjectives enter into an inclusion relation with the modified noun, giving rise to a so-called non-restrictive interpretation, subsection C discusses various types of predicative uses of adjectives, and show that the inclusion relation is also apt for describing these cases, subsection D concludes with a note on the use of attributive adjectives in complex proper nouns like de Stille Oceaan 'the Pacific' .
Set-denoting adjectives are typically used to specify the properties that are attributed to nouns or noun phrases. Two typical environments in which these adjectives occur can be distinguished: the prenominal attributive position shown in (37a) and the complementive position immediately preceding the verb(s) in clause-final position in (37b).
| a. | grote | jongens | |
| big | boys |
| b. | dat | de jongens | groot | zijn. | |
| that | the boys | big | are | ||
| 'that the boys are big.' | |||||
However, the formulation that set-denoting adjectives specify the properties of nouns or noun phrases is still too general, since there is a difference in function between the adjectives in (37a) and (37b): due to the placement of the adjective in the prenominal attributive position in (37a), the noun phrase grote jongens denotes those entities that are both big and a boy, that is, it denotes the intersection of the two sets denoted by, respectively, jongen and groot . Thus, in the domain of discourse we have set up in Figure 1, this noun phrase refers to “Jan" and “Henk". The predicative use of the adjective in (37b), on the other hand, asserts that (all of) the boys are big, that is, that we are dealing with an inclusion relation between the set of entities referred to by the noun phrase the boys and the set denoted by big . Clearly, this inclusion relation does not hold in our domain of discourse in Figure 1, since “Peter" is not included in the set of big . This difference between the attributive and predicative use of the set-denoting adjectives can be schematically represented as in Figure 2.
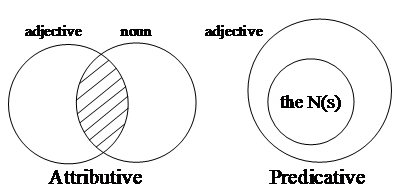
The intersection relation between the noun and the attributive adjective depicted in Figure 2 amounts to saying that the adjective restricts the denotation of the noun, and this reading is therefore generally referred to as the restrictive interpretation of the attributive adjective. Sometimes, however, attributive adjectives also allow a non-restrictive interpretation, and in that case their function is very similar to that of predicatively used adjectives. We will distinguish two cases that differ in whether the modified noun denotes a singleton or non-singleton set.
Both examples in (38) are fully acceptable in case there is just a single crown prince in the domain of discourse. This means that the attributively used adjectives in (38a) are not needed to restrict the denotation of the noun kroonprins 'crown prince' , but added to express additional information about the crown prince: just like the predicative adjectives in (38b), the attributive adjectives are used to inform the addressee about the fact that the crown prince is tall and fair.
| a. | De | lange, | blonde | kroonprins | trok | in China | veel aandacht. | |
| the | tall | fair | crown prince | drew | in China | much attention | ||
| 'The tall, fair crown prince got a lot of attention in China.' | ||||||||
| b. | De kroonprins | is lang en blond. | |
| the crown.prince | is tall and fair |
We need not construe the non-restrictive interpretation of (38a) as an exception to the general pattern given in Figure 2, but can simply consider it a special case of the left-hand representation. Given that the noun kroonprins denotes a singleton set, the intersection of the sets denoted by the noun and the two adjectives is either the singleton set denoted by the noun or empty. Since it would not be informative to attribute the properties of being long and fair to the empty set, it is clear that the speaker intends to refer to the singleton set; this gives the false impression that (38a) involves an inclusion relation, whereas we are actually dealing with a special case of the intersection relation.
Adjectives modifying proper nouns may also receive a non-restrictive interpretation, due to the fact that proper nouns are normally not used to denote a set, but an individual. The examples in (39a&b) therefore express that de Westerkerk can be characterized as a beautiful church, and that Schiphol is a crowded airport. Note that there is a certain tendency for non-restrictive attributive adjectives to be interpreted as epithets, example (39c) being a classical example of this.
| a. | de | mooie | Westerkerk | a church in Amsterdam | |
| the | beautiful | Westerkerk |
| b. | het drukke | Schiphol | an airport near Amsterdam | |
| the crowded | Schiphol |
| c. | de | beeldschone | Helena | |
| the | beautiful | Helen |
Note that proper nouns must always be preceded by a determiner if they are modified by an attributive adjective. The articles in (39b&c), for example, are obligatory despite the fact that the proper nouns in these examples are normally article-less: cf. (*het) Schiphol and (*de) Helena. For this, we refer the reader to the comprehensive discussion of modification of proper nouns in N3.
There is no a priori reason for assuming that the non-restrictive reading is limited to proper nouns and nouns denoting singleton sets: we expect that, at least in some cases, we will find ambiguous examples when the modified noun denotes a non-singleton set. This is indeed borne out, as will be clear from the examples in (40). These examples can all be interpreted as referring to a subset of the denotation of the noun, but they also allow a non-restrictive interpretation, in which case the property denoted by the adjective is attributed to all members of the set denoted by the noun.
| a. | De dappere soldaten | vochten | tot het einde. | |
| the brave soldiers | fought | to the end |
| b. | Het koude water | deed | Peter rillen. | |
| the cold water | did | Peter shiver | ||
| 'The cold water made Peter shiver.' | ||||
Example (40a), for example, can have two interpretations: under the restrictive reading of the adjective dappere 'brave' , it is asserted that only a subset of a larger set of soldiers fought till the end; the non-restrictive interpretation of the adjective, on the other hand, implies that all members of the set of soldiers fought to the end, for which reason they are called brave. Note that example (40a) is only truly ambiguous in written language and that, in speech, intonation will normally resolve the ambiguity: on the restrictive reading the adjective will usually be stressed, whereas it will normally be unstressed on the non-restrictive reading.
| a. | De dappere soldaten vochten | tot het einde. | restrictive |
| b. | De dappere soldaten vochten | tot het einde. | non-restrictive |
Something similar holds for (40b): under the restrictive interpretation there are several contextually determined amounts of water with different properties, and it is asserted that the water that was cold made Peter shiver: under the (more likely) non-restrictive reading, there is just one amount of water, and we will infer that the water made Peter shiver because it was cold. The ambiguity can again be dissolved by means of the intonation pattern.
| a. | Het koude water deed Peter rillen. | restrictive |
| b. | Het koude water deed Peter rillen. | non-restrictive |
Similar ambiguities may also arise in constructions with a demonstrative determiner or a possessive pronoun. Example (43a) can be used in order to ask for a certain pen from a contextually determined set of pens, in which case the adjective is used restrictively to identify the intended object. The adjective may, however, also be used if there is only one entity that answers to the description of the noun pen , in which case the adjective has a non-restrictive, purely descriptive function, which may help the addressee to recognize the object referred to, but does not serve to identify the intended object. Similarly, example (43b) can be used in a context where the speaker had an old computer that did not function well, in which case the adjective is used restrictively and will be emphasized. A non-restrictive interpretation is, however, also possible; in that case no comparison with other computers is involved, and the intended computer may in fact be the very first one the speaker ever had.
| a. | Kun | je | mij | die rode pen | aangeven? | |
| can | you | me | that red pen | prt.-hand | ||
| 'Can you hand me that red pen?' | ||||||
| b. | Mijn nieuwe computer | werkt | prima. | |
| my new computer | works | fine |
Sometimes, the context also favors the non-restrictive reading. In (44), for example, it is clearly the non-restrictive reading of the adjective that is intended: the intended message is not that only the well-informed advisors will be glad to be of service, but that all advisors are well informed and will be glad to be of service.
| Onze welingelichte adviseurs | zijn | u | graag | van dienst. | ||
| our well.informed advisors | are | you | gladly | of service | ||
| 'Our well-informed advisors are glad to be of service to you.' | ||||||
Example (45) shows that certain construction types may also favor the non-restrictive reading. The pseudo-partitive construction van die heerlijke truffels ,which is more extensively discussed in N4.1.1.6, looks like a PP but in fact functions as a noun phrase that refers not to a particular subset of truffles but to a certain type of truffles, which is claimed to be delicious. The attributive adjective does not serve to restrict the denotation of the noun, because this is assumed to be known to the addressee, but is used purely descriptively; we may infer from (45) that the speaker wants to have more truffles of the intended type, because he considers them delicious.
| Mag | ik | een half pond | van die heerlijke truffels? | ||
| may | I | a half pound | of those lovely truffles | ||
| 'Can I have half a pound of those lovely truffles?' | |||||
Indefinite noun phrases do not readily allow a non-restrictive interpretation of the attributive adjective; in all examples in (46), the adjective restricts the set denoted by the noun, thus (implicitly) contrasting this subset with the remaining members of the set.
| a. | Kun | je | mij | een rode pen | aangeven? | |
| can | you | me | a red pen | prt.-give | ||
| 'Can you hand me a red pen?' | ||||||
| b. | Nieuwe computers | werken | prima. | |
| new computers | work | excellent |
| c. | Wij | hebben | alleen | welingelichte adviseurs | in dienst. | |
| we | have | only | well.informed advisors | in employ | ||
| 'We only employ well-informed advisors.' | ||||||
The semantic representation of the predicative use of the adjective depicted in Figure 2 was based on a discussion of complementive adjectives. The set-theoretic interpretation of supplementive adjectives like dronken in (47) is, however, very similar.
| a. | De gasten | gingen | dronken | naar huis. | |
| the guests | went | drunk | to home | ||
| 'The guests went home drunk.' | |||||
| b. | Ik | bracht | de gasten | gisteren | dronken | naar huis. | |
| I | took | the guests | yesterday | drunk | to home | ||
| 'Yesterday, I took the guests home, drunk.' | |||||||
The examples in (47) express that the guests were drunk when they went/were taken home, that is, that the set denoted by de gasten 'the guests' is a subset of the set denoted by dronken . Therefore, as far as the noun phrase and the adjective are concerned, the same set-theoretical implication is expressed as in the case of the predicative use of the adjective in de gasten zijn dronken 'the guests are drunk' . For simplicity, we have ignored that (47b) is actually ambiguous and that the adjective may also be predicated of the subject ik 'I' ; we will return to this fact in Section 6.3.
The set-theoretic interpretation of appositively used adjectives is also very similar to that of the complementive adjectives: example (48a), for instance, implies that all of the men are angry about the rejection. The appositive phrase in this example can be paraphrased by means of the nonrestrictive relative clause in (48b), which contains a copular construction; see Section 6.4, sub II, for restrictive appositives.
| a. | De mannen, | kwaad over de afwijzing, | schreven | een gepeperde brief. | |
| the men | angry about the rejection | wrote | a spicy letter |
| b. | De mannen, | die kwaad | waren | over de afwijzing, | schreven | een gepeperde brief. | |
| the men | who angry | were | about the rejection | wrote | a spicy letter | ||
| 'The men, who were angry about the rejection, wrote a spicy letter.' | |||||||
The primeless examples in (49) show that adjectives are sometimes an inherent part of proper nouns. We are not dealing with attributively used adjectives in cases like these, which is clear from the fact, illustrated in (49b), that complex proper nouns like Magere Hein cannot be preceded by a definite determiner; the discussion of the examples in (39) has shown that a determiner normally must be present if a proper noun is preceded by an attributive adjective. For completeness’ sake, example (49b') shows that the complex proper noun Magere Hein does not behave differently in this respect.
| a. | de | Middellandse | zee | |
| the | Mediterranean | Sea |
| b. | (*de) | Magere Hein | |
| the | Grim Reaper |
| b'. | * | (de) | schrikaanjagende | Magere Hein |
| the | terrifying | Grim Reaper |
The examples in (50) show that an attributive adjective may sometimes also form a fixed collocation with a common noun. It would not be proper to say that the attributive adjective wit 'white' has a restrictive function in (50a): rather the adjective and the noun function as a lexical unit that refers to a certain type of wine. The adjectives in (50) are sometimes referred to as classifying adjectives; cf. Alexiadou et al. (2007:part III, §3.3).
| a. | witte wijn | 'white wine' |
| b. | magere melk | 'skim(med) milk' |
| c. | Chinese thee | 'Chinese/China tea' |
| d. | Franse kaas | 'French cheese' |
The collocations in (50) come close to compounds. In this respect we may refer to the difference between Dutch witte wijn and its German counterpart Weißwein , which does not exhibit attributive inflection and therefore must be the result of compounding; cf. Booij (2002:12). A similar contrast between Dutch and German is more or less consistently found with color adjectives in the names of animal species; this is illustrated in (51) by means of a number of bird names. taken from an extensive list found at mezen.madelen.nl/VogelnamenWereld.xls.
| a. | blauwe reiger |
| a'. | Graureiher |
| a''. | Grey Heron |
| b. | bruine vliegenvanger |
| b'. | Braunschnäpper |
| b''. | Brown Flycatcher |
| c. | gele ral |
| c'. | Gelbralle |
| c''. | Yellow Rail |
| d. | grijze spotlijster |
| d'. | Grau-Spottdrossel |
| d''. | Grey Thrasher |
| e. | rode wouw |
| e'. | Rotmilan |
| e''. | Red Kite |
| f. | witte specht |
| f'. | Weißspecht |
| f''. | White Woodpecker |
Note. however, that if the bird name is based on some characteristic body part, as in (52a), Dutch invariantly uses a compound form. This may be to avoid confusion with attributive constructions such as (52a'), although this leaves open the question why compounding is also preferred in examples such as (52b), where such confusion is not likely to arise, given that the form borstbijeneter does not exist. We will leave the contrast between the primeless examples in (51) and (52) for future research.
| a. | blauwborst | 'Bluethroat' |
| a'. | blauwe borst | 'blue throat' |
| b. | blauwborstbijeneter | 'Blue-breasted Bee Eater' |
| b'. | * | blauwe borstbijeneter |
Adverbially used adjectives are not morphologically distinguished from attributively or predicatively used adjectives in Dutch; that is, Dutch has no equivalent of the English suffix -ly. This means that the forms in (53) can be translated in English either as adjectives or as adverbs. Note that, although it is not clear whether there is a categorial distinction between the English adjectives and adverbs in (53), we will treat the adverbs in question as (inflected) adjectives here.
| a. | snel: quick (A), quickly (ADV) |
| b. | langzaam: slow (A), slowly (ADV) |
| c. | behoedzaam: cautious (A), cautiously (ADV) |
Due to the lack of morphological marking, predicative and adverbial uses of adjectives are sometimes hard to distinguish in Dutch; cf. Sections 5.2, sub IV, and 8.2.2. Often, we can only appeal to the meaning of the example to determine whether we are dealing with the former or the latter. The crucial difference between attributively and predicatively used adjectives, on the one hand, and adverbs, on the other, is that whereas the former only modify nouns and noun phrases, the latter specify VPs, APs (including adverbial phrases), and PPs. Consider the examples in (54a&b). Although the syntactic frames in which boos 'angry' and snel 'quick' are used seem identical, we are dealing with a supplementive adjective in (54a) and with an adverbially used adjective in (54b). This can be made clear by using the paraphrases in the primed examples, which show that boos modifies the noun phrase Jan , whereas snel modifies the VP weg lopen 'walk away' . The paraphrase in (54b'') may be clumsy, but the contrast with (54a'') is pretty sharp.
| a. | Jan liep | boos | weg. | |
| Jan walked | angry | away |
| a'. | Jan liep | weg, | terwijl | hij boos | was. | |
| Jan walked | away | while | he angry | was | ||
| 'Jan walked away while being angry.' | ||||||
| a''. | * | Zijn weggaan | was boos. |
| his going away | was angry |
| b. | Jan liep | snel | weg. | |
| Jan walked | quickly | away |
| b'. | * | Jan liep weg, | terwijl | hij snel | was. |
| Jan walked away | while | he quick | was |
| b''. | Zijn weglopen | was snel. | |
| his walking away | was quick |
In example (55a), too, we are dealing with an adverbially used adjective, since what is expressed is not that Jan is cautious (he may be reckless in several respects), but that the activity of investigating the meal was undertaken cautiously. Example (55b), on the other hand, is ambiguous: it can be interpreted either as meaning that Jan was greedy or as meaning that the investigation was undertaken eagerly.
| a. | Jan onderzocht | de maaltijd | behoedzaam. | |
| Jan investigated | the meal | cautiously |
| b. | Jan onderzocht | de maaltijd | gretig. | |
| Jan investigated | the meal | greedy/eagerly |
In (56a), the adverbially used adjective goed 'well' modifies an adjective. There are reasons for assuming that intensifiers like erg 'very' and afdoende 'sufficiently' in (56b&c) also belong to the adjectival class; cf. the primed examples and the discussion in Section 3.1.2.
| a. | een | goed | leesbaar | handschrift | |
| a | well | readable | handwriting |
| a'. | een | goed | handschrift | |
| a | good | handwriting |
| b. | een | erg | mooi | boek | |
| a | very | beautiful | book |
| b'. | een | erg | ongeluk | |
| a | bad | accident |
| c. | een | afdoende | gemotiveerd | antwoord | |
| a | sufficiently | motivated | answer |
| c'. | een | afdoende | antwoord | |
| a | conclusive | answer |
In (57), we are dealing with adverbially used adjectives modifying, respectively, a locational and a temporal PP.
| a. | De kerk | stond | ver | buiten het dorp. | |
| the church | stood | far | outside the village | ||
| 'The church was far from the village.' | |||||
| b. | Jan voltooide | zijn artikel | lang | voor de deadline. | |
| Jan finished | his paper | long | before the deadline |
- 2007Noun phrases in the generative perspectivenullnullBerlin/New YorkMouton de Gruyter
- 2002The morphology of DutchnullnullOxfordOxford University Press
